Simon Cotton takes a look at those compounds that find themselves in the news or relate to our everyday lives
Something to do with road surfaces?
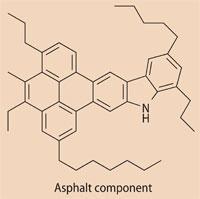
Bitumen (asphalt) is the highest-boiling point, heaviest and most polar fraction from the vacuum distillation of crude oil. Bitumen is composed of asphaltene and maltene. The heavy insoluble asphaltene molecules give bitumen its body and softening point while the maltenes are oily and make asphalt flexible. Asphaltene molecules are soluble in aromatic solvents like toluene but insoluble in heptane. The maltenes are heptane-soluble molecules and less aromatic.
So asphaltenes are aromatic?
Highly aromatic; some are hydrocarbons but many molecules contain odd heteroatoms, ie N, O, and S. There are also some metals present - V, Ni and Fe.
The asphaltene mixtures are complex combinations of molecules, but some structures are known. Reported formula masses have been controversial because of a tendency of these molecules to aggregate, but mass spectroscopic techniques shows that the most probable Mr is ca 600, with a spread in masses to above 1000.
Where do you find asphaltene-rich sources of bitumen?
Asphaltene-rich sources (over 15 per cent) include the Athabasca oil sands in Alberta, Canada and the heavy oils of Mexico (Maya oil) and Venezuela. There is more bitumen in Alberta than in the total world oil reserves, though much is exceptionally difficult to extract, if not impossible.
The 'cholesterol of petroleum'?

Because asphaltene has a big effect upon the viscosity of crude oil, it tends to block oil pipelines, and it also clogs porous rocks in oil fields. These big molecules have a low volatility and are therefore hard to ignite, and do not burn well. They also promote corrosion of pipelines. When these molecules are cracked, coke can form in the pores of the heterogeneous cracking catalyst.
So why bother with it?
Apart from road surfacing, asphaltene may become an important energy source. As the easily extractable deposits of petroleum run out, the rather intractable asphaltene will increasingly need to be extracted from the abundant oil sands.






No comments yet