By investigating the synthesis of the major antiulcer drug, esomeprazole, undergraduates are given an insight into the challenges of modern process chemistry - from optimisation of the lead compound to its full-scale manufacture.
-
A context-based practical designed to give students the opportunity to improve their team working, communication and time-management skills

Esomeprazole (1) (Nexium) is an antiulcer drug developed by AstraZeneca. With global annual sales of $5.2 billion in 2007, it is one of the world's 'blockbuster' drugs.
Esomeprazole works by selectively inhibiting an enzyme that is responsible for producing acid in the stomach. The reduction of gastric acid helps to heal ulcers. These are sores or raw areas in the stomach and upper part of the small intestine caused by infection with a bacterium or by long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Launched in 2000, esomeprazole was the first enantiomerically pure proton pump inhibitor to enter the market (Box 1).
Process chemistry
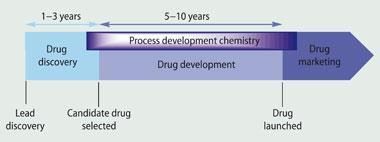
Working with AstraZeneca chemists, we have developed a third-year undergraduate project that focuses on the preparation and scale-up of esomeprazole. Our aim was to give chemistry students at York an introduction to the excitement and challenges of process development chemistry. In comparison to many other careers in the chemical industry, such as discovery chemistry, the role of a process chemist is often less well understood by undergraduates (see Fig 1).
Process chemists are responsible for identifying and developing new processes for the manufacture of chemical products. They implement controls and test methods to assess the reliability and reproducibility of the production method. This includes scaling-up a research prototype (often devised in a discovery chemistry laboratory) to pilot production (typically, from a few kilograms to 200-300 kg of material) and then to full-scale manufacture.
The method of production must meet all relevant legislation and safety regulations. In addition, process chemists are responsible for the production and delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) to support the activities of the wider project, for example, formulation and toxicological studies, as well as clinical trials.
The project
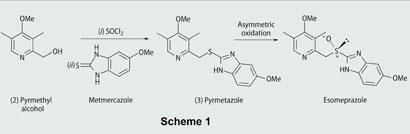
Following an introductory presentation by a process chemist from AstraZeneca, eight-10 students work as a team to prepare pyrmetazole from pyrmethyl alcohol. They then investigate the reaction conditions required to optimise the asymmetric oxidation of the sulfide group in pyrmetazole to form esomeprazole (Scheme 1).
Students do a series of small-scale oxidation reactions, using reagents and reaction conditions of their choice, to investigate how the conditions affect the efficiency of the oxidation. We emphasise that they should work together to plan their experiments to maximise the number of results they achieve over the eight-day period of the project. They then summarise their results and describe aspects of scaling-up their optimised reaction in individual reports, which are assessed.
Their results are reviewed and compared with the current industrial process in a final presentation given by an AstraZeneca chemist. By using a modern industrial context we show students the relevance of practical work in the world, which we believe will promote their enthusiasm for practical work.1-3
Asymmetric oxidation steps
The key step in the synthesis of esomeprazole is the asymmetric oxidation of the sulfide group. Students first do this oxidation reaction using the following unoptimised conditions in a two-stage process:
- Ti(Oi Pr)4 (1 equiv); S,S -DET (2 equiv); H2O (1 equiv); ethyl ethanoate (15 ml); pyrmetazole (1 equiv); at 50oC for one hour; followed by,
- triethylamine (1 equiv); cumene hydroperoxide (2 equiv); at 30oC for one hour.
Prior to the development of this process by AstraZeneca, though asymmetric oxidation methods were known (Box 2),4,5 the asymmetric oxidation of pyrmetazole to form esomeprazole in high enantiomeric excess proved elusive.
In this two-step oxidation method there are several variables that can be changed, including: the choice of reaction temperature; equivalents of reagents; solvent; concentration; and the amine base in triethylamine. Process chemists at AstraZeneca found that changes to some of these variables can affect the yield and the enantiomeric excess of esomeprazole,6 so this method gives students the opportunity to see how changes in reaction conditions can affect the efficiency of a transformation.
There are many more variations than there is time for students to investigate and so, as a group, they need to decide which ones to study, and to use the results of the initial experiments as a guide for deciding subsequent experiments. Before starting the experiment, students are required to complete a risk assessment.
We tell the students to aim for a number of reproducible, high-quality results, and to optimise the reaction to achieve a minimum yield of esomeprazole of 70 per cent. For each reaction product, the pyrmetazole:esomeprazole ratio can be determined from the 1H-nmr spectrum.
Towards the end of the project, using their optimised conditions, the students then scale-up their reaction to make 10 g of esomeprazole in a single batch reaction. They can then compare the efficiency of the small and larger-scale reactions. By slightly modifying the workup, the sodium salt of esomeprazole can be isolated and the enantiomeric excess of the salt can be estimated from the optical rotation value using polarimetry or, more accurately, by chiral HPLC.
Assessment and student feedback
An important aim of the project is for students to consider what factors need to be considered when scaling up a reaction. These factors are discussed in the introductory presentation. In an individual report, they present their results and discuss the safety implications of scaling-up their optimised reaction to a pilot plant-scale by considering:
- the physical and chemical properties of the reactants, reagents, products and wastes, including impurities;
- the potential for substances in use to corrode the plant;
- the fire and explosion hazards;
- the health hazards and personal, protective equipment assessments;
- the thermochemistry of both the desired and potential undesired reactions, in particular the rate of heat output (is a runaway exothermic reaction possible?); and
- environmental effects.
Our analysis of written and verbal student feedback has shown that students enjoy the opportunity to make such an important drug molecule on a small-scale and to learn how it can be prepared on a large-scale in the chemical industry. They are also more aware of what a career in process chemistry can offer.
For the oxidation reaction, the opportunity for students to choose their own experimental conditions is challenging and most feel that the practical work improved their team working, communication and time-management skills. They also hone their practical skills and gain much satisfaction in preparing esomeprazole in yields above 70 per cent. Students also appreciate the opportunity to discuss their work with a process chemist at the beginning and end of the project.
Future opportunities
This project could be expanded by getting the students to do a kilo-scale synthesis using their optimised conditions, which would require the use of more-specialised equipment, including a jacketed vessel.
We hope that this project will encourage others to develop context-based practicals in collaboration with the chemical industry, which we believe offers a number of benefits to the training of undergraduate chemistry students.7 It would be interesting to see the development of collaborative projects in other areas of industrial chemistry, such as discovery chemistry and materials chemistry.
Dr Andrew F. Parsons is deputy head of department and undergraduate admissions tutor in the department of chemistry at the University of York, York YO10 5DD (e-mail: afp2@york.ac.uk).
Acknowledgements
I thank Dr Steven Raw and Dr David Hollinshead (AstraZeneca) for supporting this project; Lee Duff and Matthew Palframan (York) for their help with trialling the practical work; and third-year University of York undergraduate students.
Box 1 - Proton pump inhibitors
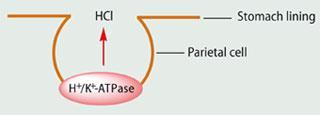
The inner surface of our stomach is lined with different types of cells, including parietal cells. A normal human stomach contains around one billion parietal cells, and it is these cells that secrete 0.16 M hydrochloric acid into the stomach. Parietal cells contain a hydrogen-potassium-adenosine triphosphatase enzyme (or H+/K+-ATPase) that actively transports protons into the stomach and is called a proton pump.
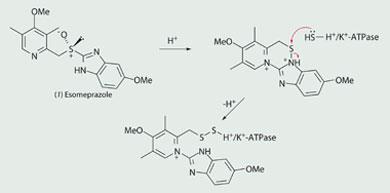
Drugs that lead to a pronounced and long-lasting reduction of gastric acid production are proton pump inhibitors, or PPIs. They work by blocking the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme in the wall of the stomach which produces the hydrochloric acid. In the acidic conditions of the stomach, esomeprazole is converted into a highly reactive sulfenamide (which contains a relatively weak N-S bond) that binds irreversibly to H+/K+-ATPase. This prevents the active transport of protons, which dramatically reduces the acid secretion of the stomach, and helps to heal ulcers and reduce the pain from indigestion and heartburn.
Box 2 - Sharpless asymmetric epoxidation
The Sharpless epoxidation reaction is one of the most synthetically useful modern reactions, which has proven to be a general and efficient method for converting allylic alcohols into epoxy alcohols in high enantiomeric excess.4 The C=C bond of an allylic alcohol is converted into an epoxide using a titanium catalyst (titanium tetraisopropoxide), a chiral ligand (either l-(+)-diethyl tartrate or d-(-)-diethyl tartrate) and an oxidant such as a hydroperoxide (see Scheme).
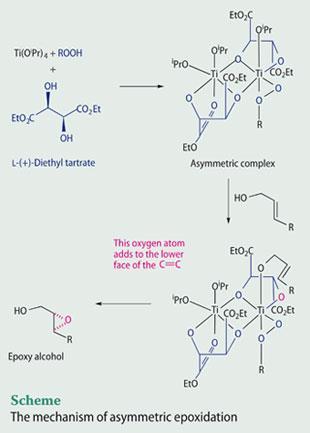
As a consequence of the importance of this method, there have been many studies to probe the reaction mechanism.5 The active catalyst is likely to be a complex containing two titanium atoms, bridged by two tartrate ligands, and the oxidant, which is coordinated to a titanium atom. During the epoxidation reaction, the allylic alcohol becomes coordinated to the titanium atom bearing the oxidant. Then, because of the shape of the complex, an oxygen atom from the oxidant is selectively delivered to only one face of the C=C bond.
References
- D. Lennon et al, Green Chem., 2002, 4, 181.
- D. J. McGarvey, Educ. Chem., 2007, 44 (4), 116.
- D. J. McGarvey, New Directions in the Teach. of Phys. Sci., 2006, 2, 57.
- T. Katsuki and V. S. Martin, Org. React., 1996, 48, 1.
- M. G. Finn and K. B. Sharpless, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 113.
- H. Cotton et al, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2000, 11, 3819.
- A. Merritt, Drug Discov. Today, 2001, 6, 287.






No comments yet