Retrieve information on the metallic bonding model and explain how this leads to particular properties in metals
This resource is part of our support for literacy in science teaching, embedding literacy into your curriculum and developing learners’ skills in reading, writing and talking about science and their understanding of scientific language.
-

Download this
Download the structure strips, which are printed five to a page, to support learners to find or retrieve information and write independently.
Find model answers in the teacher guidance.
View and download more Structure strips
Learning objectives
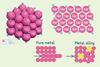
- Describe the metallic bonding model using words and diagrams.
- Explain how the metallic bonding model leads to the common properties of metals.
- Develop skills in extended writing.
Introduction
14–16 learners can probably list many of the properties of metals from their prior learning. In this activity they will use a structure strip to describe the metallic bonding model and explain how this leads to particular properties. This activity can be used as an introduction to the concept or as revision.
How to use structure strips
Structure strips are a type of scaffolding you can use to support learners to retrieve information independently. Use them to take an overview at the start of the topic, to activate prior knowledge, or to summarise learning at the end of a teaching topic. For more ideas on how to use structure strips with your learners, see 5 ways to use structure strips effectively
Structure strips have sections containing prompts which are sized to suggest the amount that learners must write. Learners glue the strips into the margin of an exercise book and write their answers next to the sections, in full sentences. When learners have finished using the structure strip, they should have an A4 page set of notes and examples.
The strips are printed five to a page and will need to be trimmed to size. Find them on the second page of the student sheet.
Scaffolding
Additional scaffolding may be required to support learners to answer the questions. These could include a list of key words or add or remove prompts in the structure strip.
As learners grow in confidence they may be able to answer the question without the structure strip or attempt the question first and then use the structure strip to improve or self-assess their answer.
Metacognition
This activity supports learners to develop their metacognitive skills in the three key areas:
- Planning: the strips provide scaffolding to plan the written response. Learners will decide where to gather information from (eg textbooks, own notes, revision websites). Ask learners: is the source of information I am using reliable?
- Monitoring: learners are prompted by the questions in the structure strip and can check their answer against the prompts. Ask learners: have you covered all of the questions in the space provided? Do you need to change anything to complete the task?
- Evaluation: learners can self-assess or ask a peer to check their work against the answers. Ask learners: did you achieve what you meant to achieve? What might you do differently next time?
Keywords
Bonding, dot and cross diagram. electron, ionic, ions, lattice, limitation, negative, positive.
Follow-up question
This question is answered after the structure strip has been attempted. The structure strip activates the required knowledge which the learners can then apply to this question.
Copper is used to make saucepans. Use your understanding of the metallic bonding model and general knowledge to explain this use of copper. [4 marks]
Answers
Suggested answers for the structure strip activity are given in the downloadable teacher notes.
Answer to follow-up question:
Indicative content for the answer
- A saucepan must be a good thermal conductor, allowing the heat from the cooker to reach the contents. (1)
- Copper is a metal.
- Metals have metallic bonding which is a regular arrangement of layers of positive metal ions (1) surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons (1).
- Metals conduct heat as the delocalised electrons are able to move through the lattice (1) and carry the heat with them.
Downloads
Metallic bonding structure strips student sheet
Handout | PDF, Size 0.13 mbMetallic bonding structure strips teacher notes and answers
Handout | PDF, Size 0.19 mbMetallic bonding structure strips student sheet
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.43 mbMetallic bonding structures strips teacher notes and answers
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.47 mb






































No comments yet