The Classical Greek period heralded an age in which thought and art flourished.
Introduction
-
Have you been on holiday to Greece? If so, did you go to Athens?
You will probably have seen the Acropolis Figure 1

Figure 1: Acropolis Hill Athens Greece.
Wikimedia Commons
An impressive and endearing building it seems, along with the sunshine, to say Greece, but there is more to Ancient Greek art.
- Did you notice the statues, frescoes, vases and reliefs?
The Acropolis of Athens and its monuments are the symbols of the classical civilisation. It represents the thoughts and spirit of an ancient people. It’s probably the greatest architectural and artistic complex of Greek Antiquity.
Ancient Greece was a set of city-states with a common religion and culture, but often competing with each other. The history of the Acropolis we see today lies in the second half of the 5th century BCE. Athens had fought and won a war against the Persians. Following the war a democracy was established and Athens took the leading position amongst the other city-states in the ancient world. There was no sharp transition from one artistic period to another but some order can be given by careful analysis of the styles of artefacts.
The Classical Greek period heralded an age in which thought and art flourished, and one in which an exceptional group of artists visualised in stone the ambitious plans of the Athenian statesman Pericles. Under the guidance of the sculptor Pheidias the rocky outcrop above the Athenian plain was transformed into a unique monument.
The important monuments built at that time were (see Figure 2):
- the Parthenon, built by Ictinus;
- the monumental entrance to the Acropolis known as the Erechtheon;
- the Propylaea, the monumental entrance to the Acropolis, designed by Mnesicles;
- and the small temple, Athena Nike.
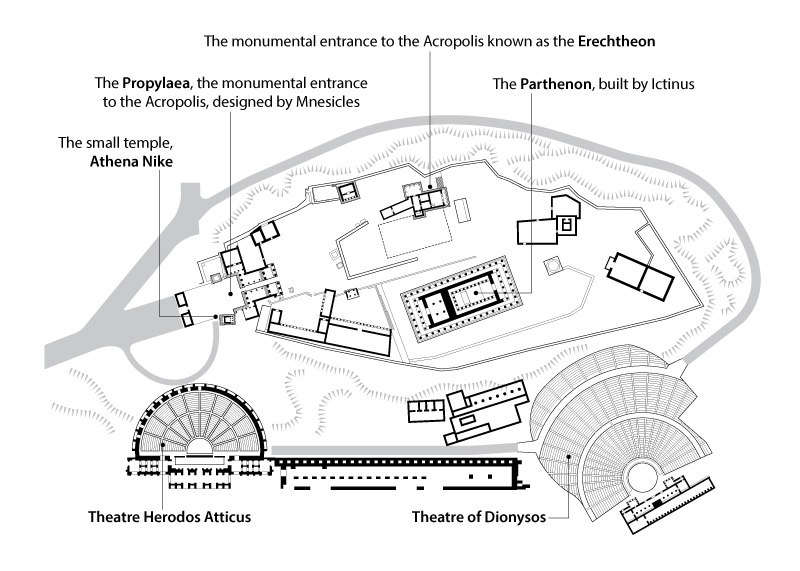
Figure 2: A plan of Acropolis Hill Athens, Greece.
Peter Bull
Where did all this classical art start?
It all started many years before the 5th century BCE. Its origins lie in the islands of Greece in the Cycladic and Minoan civilisation. As time progressed the art of the region developed and eventually gave us the Western classical art. These forms are typified in the art styles of the Geometric, Archaic and Classical periods and the Hellenistic Periods.
Cycladic art - the product of mineral wealth
The Cyclades are islands that were, as we shall see, important to the Minoans and Mycenaeans and they make up an archipelago of around 2200 islands, but only around 33 of these are inhabited. For the ancients, they formed a circle (Greek κύκλος / kyklos, hence their name) around the sacred island of Delos.
They are important because they are located at the crossroads between Europe and Asia, and the Near East and Africa. In antiquity the main travel routes were via the sea, but navigation was not easy so they sailed along the coast keeping the land in view. The nearness of the islands and their natural resources made them good places for settlement and trade as people migrated from Africa to Europe.
The area was settled from the Neolithic times and they experienced a cultural flowering in the 3rd millennium BCE. The Persians tried to take the islands during their attempts to conquer Greece, after which they entered into alliance with Athens in the Delian League. As a result Delos became a great commercial power.
The ancient Cycladic civilisation, and its art, flourished from 3300-2000 BCE mainly due to the mineral wealth on the islands. The different art styles can be grouped into three Early Cycladic periods that are not strictly time dependent but are area (see map 1) and time related:
- EC I (2800-2500 BCE) called the Grotta-Pelos Culture and best represented on the islands of Paros, Antiparos, and Amorgos;
- EC II (2500-2200 BCE) called the Keros-Syros Culture primarily seen on Syros;
- EC III (2200-2000 BCE) called the Phylakopi Culture, the art found on Milos.
From the map and the position of the islands we can see how the art has radiated out across the islands. One could hypothesis that the art moved and developed with the movement of people can be seen in Figure 3. The shape of the human form has developed and in the final image is now stylised rather than being naturalistic.
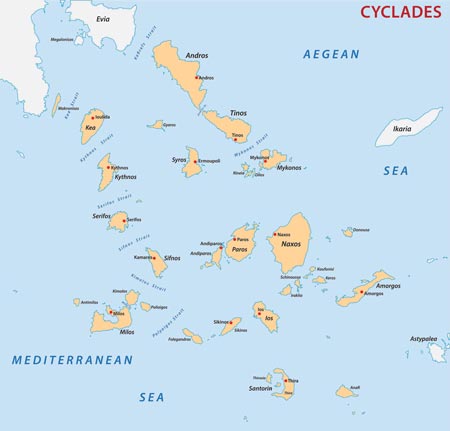
Map 1: Map of Cyclides
Shutterstock / Rainer Lesniewski
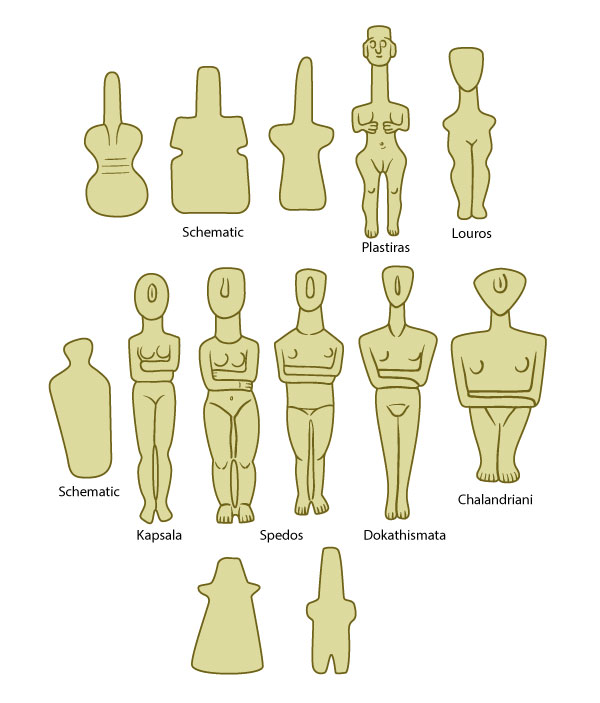
Figure 3: Early cycladic figure types - Top: types of the Gotta-Pelos culture. Middle: types of the Keros-Syros culture. Bottom: types of the Phylakopi I culture.
Peter Bull
Because of the minerals on the islands, and the islanders’ trade with other people, many of the island artists became specialists at using those materials. There is evidence of sculptors, potters, and metal-workers with blacksmiths and foundries. One example of an important local material that influenced the art was obsidian, from the island of Milos. This was the main material used for the production of tools, even after the development of metallurgy, because it was inexpensive and very sharp and could be used to cut and carve marble. Bronze tools were also used to work marble, and have been found on Naxos and Paros. At that time marble was quarried in great quantities, while today it is mined.
The bronze tools were made using copper from Kythnos. It naturally contained a lot of arsenic so the bronze was an arsenic copper alloy. It was towards the end of the Cycladian civilisation that tin was introduced to the islands. The oldest bronze tools containing tin were found at Kastri on Tinos. These have been dated to come from the Phylakopi Culture and analysis of their composition showed the tin came from Troad, an area in the Dardanelles, Turkey, near Troy. This indicated there was trade between the Troad and the Cyclades.
Naxos produced and still has quantities of an important mineral called Emery, a dark granular rock used to make abrasive powder for grinding marble. Emery largely consists of the mineral corundum Al2O3 (aluminium oxide), mixed with other minerals including magnesium aluminate MgAl2O4 (a magnesium member of the spinel mineral family), hercynite FeAl2O4 (an iron member of the spinel family), magnetite Fe3O4 (another iron member of the spinel family), and rutile TiO2 (titanium dioxide). Titanium dioxide is still used today on emery paper and boards for grinding surfaces. To fine polish the marble the artists used pumice an igneous rock from the island of Santorini.
The islands were rich in minerals that could be used as pigments. There was azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 (a copper carbonate mineral) that gave a blue colour, and haematite Fe2O3 (iron oxide) that gave a red colour. Both have been found on statuettes and in tombs see Figure 4.
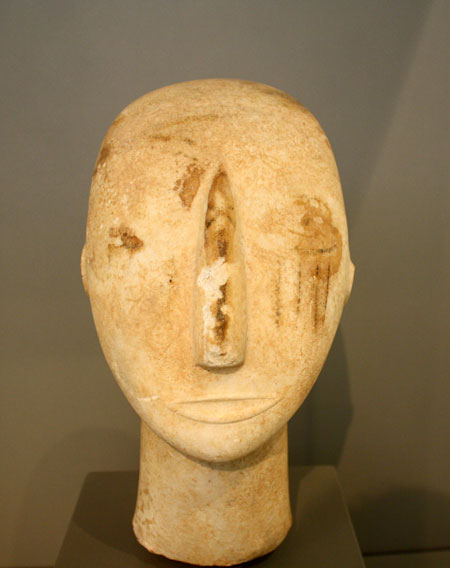

Figure 4: Cycladic Islands, Marble, (3200 - 2000 BC). Scratch or tattoos are sometimes found on face and thought to be a sign of mourning.
© World History Archive / Alamy
Cycladian art is best known for the stylised, female, nude marble sculptures. They are known as figures or idols. The most famous are the musician forms such as the harp player or pipe player see Figure 5.
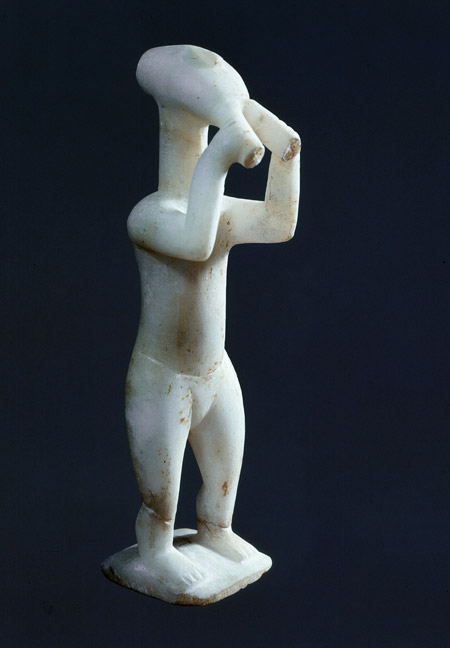
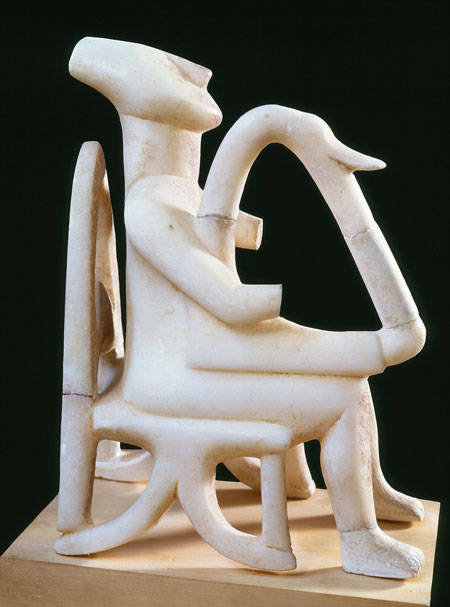


Figure 5: Harpist and double-flute player found together in a single grave on Keros. 2700-2500 BC.
From http://www.ou.edu/finearts/art/ahi4913/aegeanhtml/cyscl4.html
Figure 5: Harpist and double-flute player found together in a single grave on Keros. 2700-2500 BC.
© The Art Archive / Alamy
Others depict a human with arms folded across the stomach. These date to 2500 BCE and form some of the earliest representations of musicians from the Greek world. They are typically flat and geometric which gives them a striking resemblance to today’s modern art sculptures.
Many anthropologists believe they could be representations of a nature goddess in line with the theories of the Neolithic Venus of Willendorf, however not all archaeologists agree. There are many interpretations of their purpose from god idols to death images, and even to children’s dolls. Archaeological evidence suggests the images were regularly used in funerary practice since most have been found in graves of both men and women. Some show signs of having been repaired, implying they were objects valued by the deceased and not made specifically for burial. Larger figures were sometimes broken so only part of them was buried; a phenomenon for which there is no explanation.
The local clay on the islands proved difficult for artists to work with. Therefore the pottery, plates and vases of this period are rarely very good. Amongst the pottery found on the island of Syros were some strange objects known as ‘frying pans’, which most scholars believe were not used for cooking, but as fertility charms or mirrors.
Minoan art from the celebration of life
The Minoan civilisation, an Aegean Bronze Age civilisation, arose on the island of Crete. Flourishing from around the 27th century BCE to the 15th century BCE it was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Arthur Evans.
Minoan art tells of a people who were keen observers of their world, in touch with the environment and enjoying the world they lived in. The greatest collection of Minoan art is still on Crete in the museum at Heraklion, near Knossos.
Minoan art, with other remains, has been used by archaeologists to define the three phases of Minoan culture. These are based on pottery styles and were created by Evans and modified by later archaeologists. They divide the Minoan period into three main eras:
- Early Minoan (EM) 3650-2160 BCE
- Middle Minoan (MM) 2160-1600 BCE
- Late Minoan (LM) 1600-1170 BCE.
Wood and textiles from this time have been lost through decomposition, so the best preserved Minoan art forms are the palace architecture with frescos that include landscapes, pottery, stone carvings and intricately carved seal stones. Not much art has survived from the Early Minoan (EM) period. What has been found, in sites throughout the island of Crete? Are Cycladic statuettes and pottery fragments indicating trade across the Aegean islands?
The climax of Minoan art was reached during the Middle Minoan (MM) period reflecting a time of extraordinary development, while the art of the Later Minoan (LM) period echoes the decline of the Minoan civilisation.
Ceramics have been used as a dating method by archaeologists because of their characteristic designs. In the EM period the ceramics were characterised by linear and geometric patterns such as spirals, triangles, curved lines, crosses and fishbone motifs. This simple style developed in the MM period into representative natural designs, such as fish, squid, birds and lilies. In the LM period the flowers and animals were still present but in greater variety.
Minoan frescoes
At the end of the EM period we see the appearance of palaces, particularly around Knossos. On the walls of the palaces were frescoes; some of the only paintings to remain from the period today. The palace frescoes are characterised by geometric simplification of natural shapes and monochromatic paintings. Frescoes were the main form of Minoan art during the EM period. Along with decorated pottery, they are often the only record of just how the world appeared to the Minoans and between them they give us some tantalising glimpses of their beliefs, cultural practices and aesthetic tastes.
The early Minoan frescoes are limited to simple monochrome walls, often red sometimes black. As the Minoans improved their techniques and quality of plaster and pigments, the style began to change with possible influence from Egypt and the Near East.
Minoan paintings display Egyptian influences in the style of the figures. They are painted with a frontal style and the figures are outlined then painted. Yet it is by no means a direct copy of Egyptian style since the figures have a distinctly Minoan style. In fact the Minoan style influenced other culture’s fresco painting. The small waist, fluidity of line, and vitality of character is bestowed on every painted figure and the Minoan style conventions emphasised elasticity, spontaneity, and dynamic motion. The colours and high-contrast patterns give the characters and nature scenes an elegant freshness.
The developing style used natural subjects. This included flowers such as lilies, irises, crocuses and roses, and plants such as ivy and reeds. The Minoans were one of the earliest cultures to paint natural landscapes without humans present in the scene.
Animals were also common; monkeys, birds, cats, goats, deer, sea urchins, dolphins and fish, many frequently in their natural habitat. Minoan frescoes were often framed with decorative borders of geometric designs but the principal fresco itself could extend beyond the conventional boundaries to cover several walls creating a panorama.
Dry and wet frescoes
The “dry-fresco” (fresco secco) technique involves the application of paint, in particular for details, onto dry plaster. The “true” or “wet” painting method (buon fresco), on the other hand, involves painting on wet plaster so that the pigments are absorbed and bind well to the wall plaster. This fixes the painting and stops it from fading.
Egyptian painters painted their walls in the fresco secco technique but the Minoans used the buon fresco method. The difficulty with the buon fresco method was it required accurate and quick execution, but it had the advantage of allowing for a high degree of improvisation and spontaneity. Because the artists had to work within strict time constraints they had to be skilful. Their brush strokes needed to be fluid and graceful, and yet the chance in the art produced excitement. It is probably that which characterises Minoan painting and makes the wet method of painting the most appropriate see Figure 6.

Figure 6: Fragments of Minoan fresco paintings from 1450–1375 BCE (LM II)
© The Trustees of the British Museum
Low relief was used in the plaster to give a shallow three-dimensional effect. No surviving examples of shading effects have been found in Minoan frescoes, although the colour of the background changes whilst the foreground subjects remain unchanged. Some of the Egyptian colour conventions were adopted by the Minoans: male skin is usually red, female skin white, and the metal gold is yellow, silver is blue and bronze is red. Fresco was also used on walls to imitate architectural features, such as veined alabaster slabs painted on the lower portions of walls.
Pigments used for the colours were:
- black - carbonaceous shale;
- red - haematite (iron oxide Fe2O3);
- white - hydrate of lime (calcium oxide Ca(OH)2);
- yellow ochre - goethite (iron oxyhydroxide FeO(OH));
- blue - Egyptian Blue (copper silicate CaCuSi4O10);
- and green - blue and yellow mixed.
Frescoes are inherently fragile and often have been painted by anonymous artists. The ravages of time frequently leave them incomplete and archaeology can leave them removed from their original environment. This can make interpretation and dating difficult, and has lead to some restoration being more imaginative than accurate.
Columns and gemstones
Within the palaces another feature was common; the Minoan column. It is wider at the top than the bottom, and is called an ‘inverted’ column because most Greek columns are wider at the bottom creating an illusion of greater height. These Minoan columns were made of wood, generally painted red, mounted on a simple stone base and topped with a pillow-like, round piece as a capital.
Some Minoan artisans worked with gemstones to create seal stones. They have been found in large quantities at Knossos, Mallia and Phaistos. These are amulets about 3cm (in diameter?) but some have been found that are larger.
Mycenaean Greece
The Mycenaean Period was from around 1600 to 1100 BCE. Mycenaean Greece takes its name from the Bronze Age archaeological site of Mycenae in Argolis, Peloponnese, on the mainland of southern Greece. Mycenaean settlements have also been found in other parts of Greece including Epirus, Macedonia, on islands in the Aegean Sea, and on the coasts of Turkey, Cyprus and Italy.
Mycenaean Greece flourished under influences from Minoan Crete and the Cyclades during the Late Helladic (LH) period (1550-1060 BCE). Late Helladic pottery typically stored such goods as olive oil and wine, and the potters sometimes inscribed their work in Linear B, a syllabic script recognisable as a form of Greek. The LH period is divided into I, II, and III. LH I and II overlap with Late Minoan (LM) ware and III overtakes it. LH III is further subdivided into IIIA, IIIB and IIIC.
Pottery has been used as a dating tool because the Mycenaean people were great potters and made a great deal of pottery in many different styles. Archaeologists have found a number of widely diverse sizes and styles. They have found stirrup jars, pitchers, kraters and chalices known as ‘champagne coupes’ because of their shape. They produced pottery in great numbers and so they exported large quantities of luxurious pots featuring heavily worked painted decorations incorporating mythic, warrior or animal motifs.
Mycenaean metal-workers usually worked in bronze and made tripods, basins and lamps.
The painting of the Mycenaean age was influenced by the Minoans. Fragments of wall paintings have been found in or around the palaces at Pylos, Mycenae and Tiryns, and in some domestic contexts. The largest complete wall painting depicts three female figures, probably goddesses, in the so-called Cult Centre at Mycenae. It shows hunting, bull leaping, battle scenes and processions. Other frescoes include geometric or stylised motifs, also used on painted pottery see Figure 7.

Figure 7: Mycenaean Pottery from 1400–1350 BCE (LNIIIaI)
© The Trustees of the British Museum
Archaic Period
The Archaic period was between 800 BCE and 480 BCE. It saw the rise of the city-states (polis), the founding of colonies and the blooming of classical philosophy, theatre and poetry, which appeared with the reintroduction of the written language, lost during the Greek Dark Ages.
The term archaic takes its name from what, in art history, was considered the old-fashioned style of sculpture and other forms of art and craft characteristic of that time, as opposed to the more natural look of work in the following Classical period. During this period a massive import of raw materials including metals, and a new mobility among craftsmen, caused new craft skills to be introduced in Greece.
The following three periods have been identified:
- Early Archaic (660-580 BCE)
- Mid Archaic (580-535 BCE)
- Late Archaic (540-480 BCE).
The Archaic period is famous for its sculptures, both free-standing and in relief, used to adorn temples and funerary monuments. These were made from limestone, marble, terracotta, wood, bronze and rarer metals. During the Early Archaic period the major sculptural forms were the kouros (free-standing ancient Greek sculptures which first appear in the Archaic period in Greece they are life sized and represent nude male youths), and its female equivalent is the kore.
Archaic pottery
Also common in the Archaic period was pottery made for everyday use, and as the trophies won at games. It developed the orientalising style (marked by floral and animal motifs), signalling a shift away from the geometric style of the earlier Dark Ages, and the accumulation of influences from Phoenicia and Syria.
The styles associated with the later part of the Archaic period are black-figure pottery originating from Corinth during the 7th century BCE. The later styles were known as the red-figure style, developed by the Andokides painter. He was an ancient Athenian vase painter named after Andokides, the potter for whom he worked actively from 530 to approximately 515 BCE. His work is unsigned and typified by the Egyptian-like ‘left foot forward’, the ‘archaic smile’, and the very patterned and conventionalised hair, or ‘helmet hair’. Greek pottery is frequently signed, sometimes by the potter or master of the pottery, but only occasionally by the painter see Figure 8.
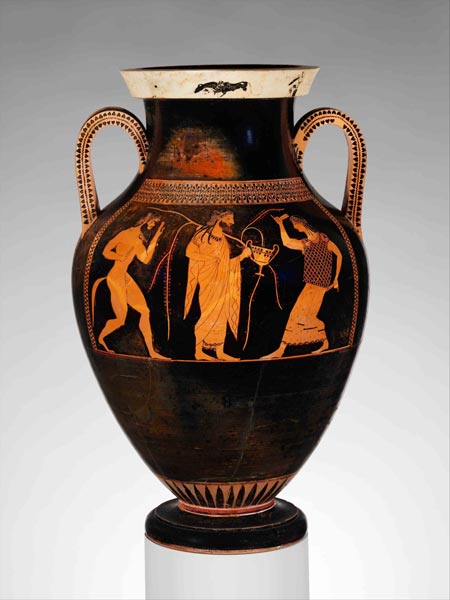

Figure 8: Bilingual amphora by the
Andokides Painter, c520 BCE (Munich)
Figure 8: Bilingual amphora by the Andokides Painter, c525 BCE (Munich)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, www.metmuseum.org
By the later Archaic and early Classical period, however, the two great commercial powers, Corinth and Athens, had come to dominate the culture and trade. Their pottery was exported all over the Greek world, driving out local varieties and going as far afield as Spain, Ukraine and Italy. Many of these pots were mass-produced products of low quality. By the 5th century BCE, pottery had become an industry and pottery painting ceased to be an important art form.
Colour and decoration
During the Archaic period the range of colours used on pots was restricted by the technology of firing: black, white, red, and yellow were the most common. In the three earlier periods, the pots were left their natural light colour, and were decorated with slip that turned black in the kiln.
In later periods, as the aesthetic shifted and the technical proficiency of potters improved, decorations took the form of human figures, usually representing the gods or the heroes of Greek history and mythology. Battle and hunting scenes were also popular, since they allowed the depiction of the horse, which the Greeks held in high esteem. In later periods erotic themes, both heterosexual and homosexual, became common.
Classical Period (510-323BCE)
The Classical Period was a 200 year period in Greek culture. In the Classical period there was a revolution in Greek statuary, usually associated with the introduction of democracy changes in the style and function of sculpture. Poses became more naturalistic. The technical skill of Greek sculptors in depicting the human form in a variety of poses greatly increased and from about 500 BCE the statues began to depict real people.
The great temples of the Classical era such as the Parthenon in Athens, and the Temple of Zeus at Olympia were built. These required relief sculpture for decorative friezes, and sculpture in the round to fill the triangular fields of the pediments so sculptures and statues were put to wider uses presenting aesthetic and technical challenge which stimulated much sculptural innovation. Unfortunately these works survive only in fragments, the most famous of which are the Parthenon Marbles, half of which are in the British Museum.

Figure 9: Family group on a grave marker from Athens
Image Courtesy of Ricardo André Frantz / Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0
Funeral statuary evolved during the Classical period and highly personal family groups of the Classical period began to be seen. These monuments are commonly found in the outskirts of Athens, which in ancient times were cemeteries. Some of depict “ideal” people the mourning mothers, the dutiful sons, but as time went on they increasingly depicted real people, typically showing the departed taking his dignified leave from his family. They are among the most intimate and affecting remains of the Ancient Greeks see Figure 9.
Hellenistic art
The Hellenistic period dates from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BCE to the emergence of ancient Rome, marked by the Battle of Actium in 31 BCE and the subsequent conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt in 30 BCE. In the Archaic and Classical art, the sculptures were generally static and idealised the archaic sculptures showed no or little emotion the Classical began to show some emotion. Classical architecture was ‘perfectly’ modelled and highly organized. However the Hellenistic sculptures became more active, dynamic, and realistic displaying a wider range of emotion. Hellenistic architecture became more grandiose and ornamented.
Frescoes
Few examples of Greek wall paintings from the Hellenistic period have survived but it was very influential on the Roman frescoes, for example those of Pompeii or Herculaneum. The few examples that survive are in archaeological discoveries at Alexandria. Here six funerary stele (a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected as a monument), in what is known as TheSoldier’s Tomb, are exceptionally well preserved Greek paintings from the Ptolemaic period of the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE.
More recently found examples of Greek wall paintings can be seen at the cemetery of Pagasae close to modern Volos, at Vergina in the former kingdom of Macedonia which are Classical in style, or those at Paestum which are really Lucanian since the Lucanians conquered and occupied Paestum, but Greek culture continued to survive and even flourish so the painting are often grouped as Greek in influence.
One of the best preserved frescoes is at the Tomb of the Diver at Paestum. Discovered in 1968 at the Tempa del Prete necropolis on the southern limits of Paestum, it is a beautiful example of Greek tomb painting and possibly the only complete Greek wall painting. The tomb is made of five limestone blocks, all from a local source. It shows a symposium (drinking group) or banquet scene extending over four stone slabs that make up the walls of the tomb and on the lid slab is a young man diving see Figure 10 & 11. It is after this image that the tomb is known. It is dated to 480 – 470 BCE.
The paintings are fresco style. Plaster was applied to the stone, and the main features were outlined using a pointed tool (stylus) and coloured red while the plaster was still fresh. The colours used were black, varying shades of red, blue, green and white. Once the flesh tones had been painted onto the stone the anatomical outline was painted in black to pick out the human shape.

Figure 10: The lid of the Tomb of the Diver Paestum
© charistoone-images / Alamy
The art of the Tomb of the Diver is essentially Greek in character with some Etruscan influences but is a good example of the type and form of art at this time of Classical Greece.

Figure 11: Symposium or banquet scene on the north wall Cortege of guests on the west wall
© PRISMA ARCHIVO / Alamy and © VPC Travel Photo / Alamy
Mosaics
It appears that during the time of the Ancient Greeks the mosaic developed. In fact they are responsible for the invention of tessellated mosaics (the tiling of a flat floor or wall using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps). The largest numbers of early types of mosaics seem to be from fine pavements from the mid-second century onwards.
The earliest known examples of mosaics made of different materials were found at a temple building in Abra, Mesopotamia, and are dated to the second half of 3rd millennium BCE. They consist of pieces of coloured stones, shells and ivory. Despite there being some simple examples of tessellation in some 3rd century BCE mosaics it is not known how or where and when innovation took place.
Mosaic work started with pebbles such as those at Pella see Figure 12a and went on to the highly refined forms such as those found at Pergamum and Alexandria see Figure 12b. It was also from about this time that the mosaic found its way into the private home as a form of decoration and this is found all the way from the edges of India across to Spain.

Figure 12a: Pebble mosaic at Pella Abduction of Helen by Theseus
© QEDimages / Alamy

Figure 12b: Greek mosaic, a deer hunt, Signed “Gnosis created”
© Image Asset Management Ltd. / Alamy
Pottery
Perhaps the most well-known art form from the Greek period is the painted and relief style pottery. On some of the pots and vases the painting was applied after firing since the pigments used for painting were unstable at high temperatures and because of this fragility they were frequently used for funerary pots. The best forms of this style have been found at Centuripe in Sicily, where a workshop was active until the 3rd century BCE.
The more well-known red and black pottery comes from the period between 6th to 4th centuries BCE and used in Athens as valuable pottery. Everyday ware was plain, simple, fired red clay. In the forming of both fine valuable and plain pottery the potter used a wheel to turn and shape the pot, and with large pots this was done in sections which were then assembled into the whole pot after sun drying and before firing. The slip was applied leaving the shapes in red and when fired the slip would turn black.
Firing
The firing process of both red and black vessels was a single phase but consisted of three stages:
The first stage was made with all the vents open allowing oxidation to take place. Air was allowed into the kiln turning the whole vase the colour of the clay. The heat and oxygen turned both the pot and slip a reddish-brown due to the formation of haematite (Fe2O3) in both the paint and the clay body.
In the second stage the air vents were partially closed so the oxygen content was reduced. Green wood was introduced to the kiln, which caused the object to turn black in the smoky environment. These conditions created carbon monoxide, which turned the red haematite to black magnetite (Fe3O4), and the temperature decreased due to incomplete combustion. In the second phase, the chemical composition of the slip surface is altered and cannot be oxidised so it remains black. This process known as the ‘iron reduction technique’ produced a striking black surface with a metallic sheen.
In the last, third stage, air was let back into the kiln causing the reserved portions to turn orange while the glazed areas remained black. The slip was thought to be a fine suspension (colloid) of illitic clay with very low calcium oxide content and rich in iron oxides and hydroxides, making this surface different from the clay used for the body of the vase.
Sculpture
The other art form the Greeks are famous for is the sculptured statue. Over the centuries the sculptures became more realistic, less austere and often showing emotion. The form is still dominated by the naked male, especially the athlete, but over the Hellenistic period there is a greater variety of subjects, poses and an interest in individuals such as rulers, philosophers, generals, politicians, orators and poets as well as the common people.
Hellenistic sculpture is identified by the ‘perfect’ sculpture. This allowed the statue to be viewed from all angles. To fabricate the sculpture the artist had to study draping, the effects of transparency of clothing, expression and character of the subject to create atmosphere. The artist explores themes such as suffering, sleep or old age and statues begin to appear in groups both mythological and historical. Pergamum becomes the place for statues and the work found there is often called Hellenistic Baroque.
The Elgin marbles
Examples of the Hellenistic style can be seen in the range of statues from this period on display at the British Museum, London. The Elgin Room contains the Parthenon marbles; pieces of sculptures removed from the Parthenon by Thomas Bruce, Earl of Elgin during 1801-05 see Figure 13.
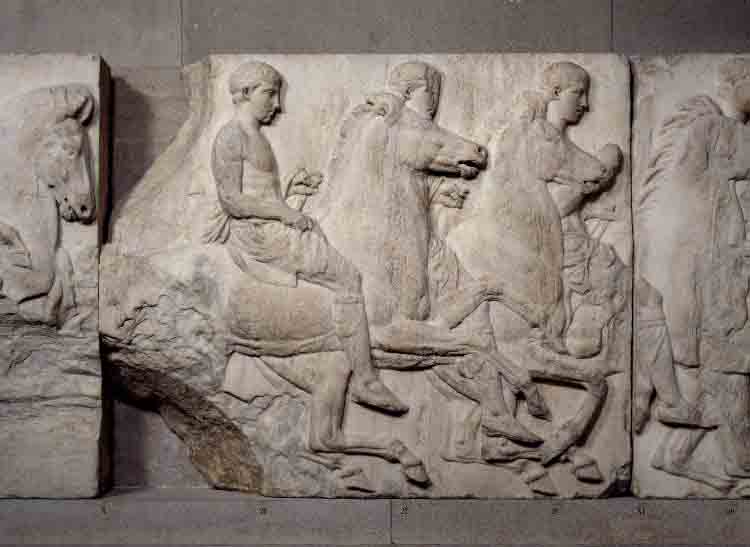

Figure 13: Riders from the pediment of the Parthenon from the Elgin Room
From the British Museum, © The Trustees of the British Museum
Figure 13: Riders from the pediment of the Parthenon from the Elgin Room
© The Trustees of the British Museum
Built nearly 2500 years ago the Parthenon was a temple dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena. For a thousand years it was the church of the Virgin Mary of the Athenians, a mosque. Now it is an archaeological ruin undergoing restoration. The sculptures have been damaged over the course of the centuries especially when the city was under siege by the Venetians in 1687. The Parthenon itself was being used as a gunpowder store when a huge explosion blew the roof off and destroyed a large portion of the remaining sculptures. The building has been a ruin ever since.
By 1800 only about half of the original sculptural decoration remained so Lord Elgin, the British ambassador to the Ottoman Empire, (Athens had been part of the Ottoman Empire for about 350 years), decided to remove half of the remaining sculptures. He acted with the full knowledge and permission of the Ottoman authorities. Being passionate about ancient Greek art he transported the sculptures back to Britain. The arrival of the sculptures in London regenerated interest in Ancient Greek culture and influenced contemporary artistic trends.
In 1816 many of the sculptures were obtained by the British Museum and since then have been on display to the public. Others were taken to Musée du Louvre, Paris, Vatican Museums, National Museum, Copenhagen, Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna, University Museum, Würzburg and the Glyptothek, Munich.
Painted marble
The pieces shown above were sculptured by Phidias and decorated the top of the Parthenon. They were meant to be seen from a distance and to help this they had been coloured.
More work on other Greek statues shows that many of them were painted as were the temples that housed them. Time and weather have stripped most of the hues away and so, as they were excavated from the soil or fished out of the sea, the statues appeared as white marble. So, since the Renaissance, the accepted colour for sculptures has been white in view of the perceived ancient aesthetic. In fact in some extreme situations restorers scrubbed off any pigment found on the statue.

















