A decision tree is a visual representation of the schema an expert might use to find the answer to a question
This resource supports the article Scaffold learning with decision trees where you can find more ideas for how to make and use decision trees in your teaching.
Introduction
25.0 cm3 of a 0.400 mol dm-3 solution of NaOH is added to 25.0 cm3 of a 1.00 mol dm-3 solution of ethanoic acid. How can you calculate the pH of the solution formed?
How to use this resource
A decision tree is a visual representation of the route you take to find an answer. It plans out thinking and breaks it down into a series of decisions to make. A decision tree can support learners by scaffolding that thinking to help them access the knowledge they need to answer questions.
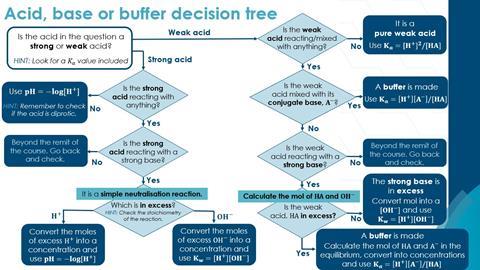
Try using this pre-prepared decision tree to aid with questions on the challenging topic of acids, bases and buffers.
- Introduce the decision tree – try using it for an example problem.
- Be prepared to modify it, add hints or recap learning if any sticking points arise.
- Gradually remove the scaffold the decision tree provides by using spaced retrieval activities carefully designed to support retention of the key decisions or knowledge.
More resources
- Try the Decision tree: what type of bonding? which includes animation to show it in use.
- Find more ideas about how and when to use decision trees in your classroom in Growing decision trees.
- The benefits of decision-based learning offers insight into education research on this topic.
Downloads
Decision tree - acid base or buffer presentation
Presentation | PDF, Size 0.49 mbDecision tree - acid base or buffer presentation
Editable handout | PowerPoint, Size 2.95 mb






















No comments yet