An investigative practical that shows students the use of chemistry in their every day lives
Create foam in your leaning space with easy to access chemicals, and household ingredients.
This experiment should take 20 minutes.
Equipment
Apparatus
- Eye protection
- Beaker, 250 cm3, x2
- Pestle
- Mortar
Chemicals
- Laundry detergent – eg Persil non-biological
- Hydrated aluminium sulfate
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Health, safety and technical notes
- Read our standard health and safety guidance.
- Always wear eye protection.
- Aluminium sulfate can cause eye damage, see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC002b.
- Laundry detergent may irritate the skin.
Procedure
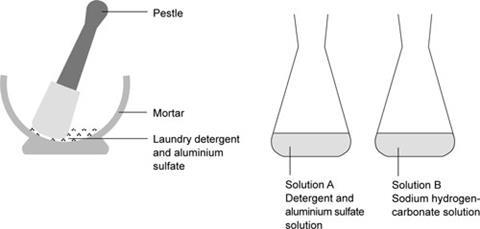
- Put 1 g of laundry detergent and 7 g of aluminium sulfate in a mortar and grind into a fine powder with a pestle.
- Dissolve this powder in approximately 50 cm3 of water in a conical flask (A).
- Dissolve 5 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate in 50 cm3 water in another conical flask (B).
- Pour the contents of flask A into flask B and mix quickly.
Notes
- It is sometimes difficult to dissolve these reagents, but the reaction still works.
- The foam is produced by the action of carbon dioxide gas on a detergent solution.
- Hydrogen carbonate ions from the detergent react with hydroxonium ions from the aluminium sulfate and water to produce carbon dioxide.
- HCO3–(aq) + H3O+(aq) → 2H2O(l) + CO2(g)
- Teachers need to tell students that aluminium sulfate in water produces H3O+ ions.
- This is similar to the baking process; baking powder contains sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid.
- This chemical foam contains carbon dioxide (CO2), while mechanical foams often contain air.
- This foam is a colloidal system with a gas dispersed in a liquid.
- This is a suspension of gas in the liquid.
- Other common foams include whipped cream and shaving cream.
Questions
- What reactions lead to the production of the foam?
- How is this reaction similar to that involving the production of carbon dioxide (CO2) during the baking process?
- Name some other examples of foams.
Answers
- HCO3–(aq) + H3O+(aq) → 2H2O(l) + CO2(g)
- Baking powder contains sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid.
- Whipped cream and shaving cream.
Downloads
Producing a foam - teacher notes
PDF, Size 0.12 mbProducing a foam - student sheet
PDF, Size 0.15 mb
Additional information
This practical is part of our Classic chemistry experiments collection.
















No comments yet