The distinction between chemical and physical change is not absolute, and there are examples of changes which teachers find difficult to classify
Students are often expected to distinguish between chemical and physical changes early in their study of chemistry, but some find this quite difficult.
Teachers suggested that this ‘could be a useful teaching tool’ that helped ‘to clarify the idea in some pupils’ minds’.
Changes in chemistry - questions
In science, we describe the changes that occur to substances as either physical changes or chemical changes. Explain what you think these terms mean:
- A physical change
- A chemical change
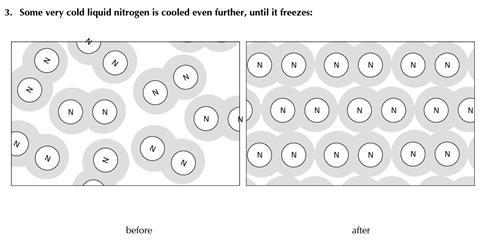
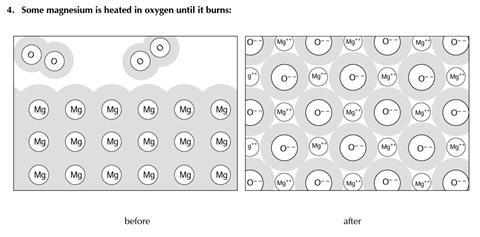
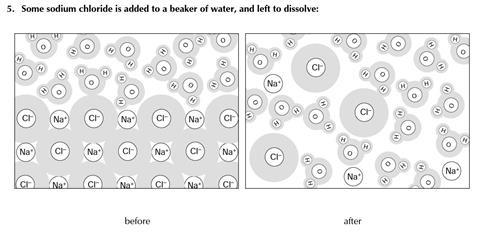
You will find three examples of substances being changed. The diagrams show some of the molecules or other particles before and after the change. For each example:
- Decide whether the change is physical or chemical
- Try to explain your reasons.
Changes in chemistry - answers
- A physical change is a change where no new substance is produced. (….a change that does not involve the breaking/forming of strong chemical bonds.) (…..a change where molecules/ions etc are rearranged, but not changed.)
- A chemical change is a change where a new substance is produced. (…..a change that involves the breaking/forming of strong chemical bonds.) (…..a change where new molecules/ions etc are formed.)
- Physical change
- No new substance is produced (the same molecules are present before and after the change)
- The change may readily be reversed
- The energy change involved is modest
- Chemical change
- A new substance is formed (strong chemical bonds are broken – egin the oxygen molecules - and new chemical bonds are formed in the metal oxide)
- Different particles are present after the change - oxide ions rather than oxygen molecules
- This change is not easily reversed
- A great deal of energy is often given out in this change
- Physical change
- No new substance is formed (NB the solution is not a pure substance, but a mixture)
- The same particles are present after the change as before
- This reaction is readily reversed – by evaporation
- The energy change for dissolving is minimal
- Note, however, that the ionic bonds in the lattice have been disrupted, which may suggest dissolving could be considered as a chemical change.
Notes
For the full version of this chapter, see downloads below.
Downloads
Changes in chemistry
PDF, Size 0.42 mb
Websites
Additional information
These resources have been taken from the book, Chemical Misconceptions : Prevention, diagnosis and care: Theoretical background, Volume 2, by Keith Taber.

Chemical misconceptions

Discover classroom strategies and activities to tackle common misconceptions among students in chemistry, and explore the theory behind different approaches.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
 Currently
reading
Currently
reading
Changes in chemistry
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36




























































































No comments yet