Use concept mapping to identify students’ alternative conceptions about acids and alkalis
Concept maps provide an alternative to linear notes and summaries that will appeal to some students
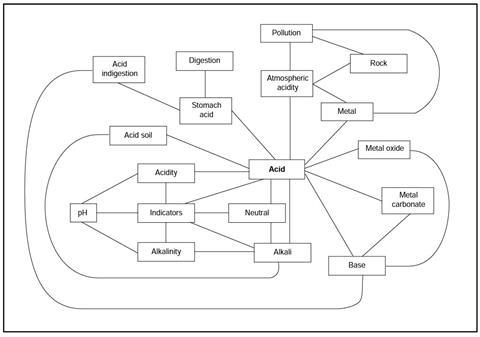
Acid concept map
You have been given a copy of the acid revision map.
This shows some of the important ideas you may have met when you studied acids and bases in your science class. Each line on the map stands for an idea that could be put into a sentence.
The links are not explained on the map.
Read through the statements below, and work out which link on the map each sentence is about.
Label each line on the map with the number of the statement
Find out how to use an enhanced version of this resource with your students to revise acids and alkalis using concept maps.
- Acidity is a property of acids.
- Acids can be identified using indicators.
- Acidity can be measured using the pH scale.
- Acidity can be detected using an indicator.
- Alkalinity is a property of alkalis.
- Alkalinity can be detected using an indicator.
- Alkalinity can be measured using the pH scale.
- Neutral solutions can be identified using indicators.
- Alkalis can be identified using indicators.
- Acids are not neutral solutions.
- Alkalis are not neutral solutions.
- pH may be found using universal indicator.
- Acids react with alkalis to give a salt and water.
- Bases react with acids.
- An alkali is a base which dissolves in water.
- Metal carbonates are bases.
- Metal carbonates react with acids to give a salt and carbon dioxide.
- Metal oxides are bases.
- Metal oxides react with acids to give salts and water.
- Some metals react with acid to give a salt and hydrogen.
- Acids in the air cause atmospheric acidity.
- Atmospheric acidity is increased by some forms of pollution.
- Atmospheric acidity causes weathering of rocks.
- Pollution can increase the rate of weathering of rock.
- Atmospheric acidity causes the corrosion of some metals.
- Pollution can increase the rate of corrosion of metals.
- Acid is found in the stomach.
- Stomach acid helps us digest our food.
- Too much stomach acid can cause indigestion.
- Some bases are used to relieve acid indigestion.
- Some soils contain too much acid for most plants to grow.
- An alkali is sometimes added to soil to neutralise acidity.
Completing the map labels
You have been given a copy of the acid revision map.
This shows some of the important ideas you may have met when you studied acids and bases in your science class. Each line on the map stands for an idea that could be put into a sentence. The links are not explained on the map.
Read through the statements below, and work out which link on the map each sentence is about.
However, each sentence has a key word or phrase missing, so you will also need to complete the sentences!
Label each line on the map with the number of the statement.
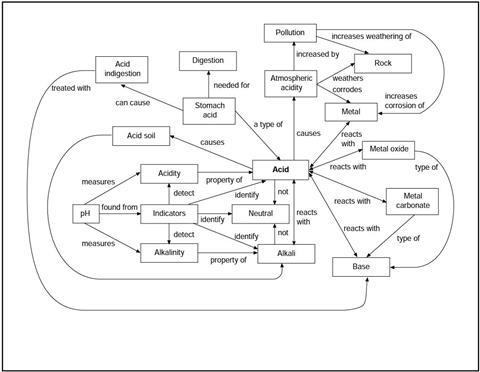
- Acids in the ______________ cause atmospheric acidity.
- Atmospheric acidity is increased by some forms of ______________.
- ______________ ______________ causes weathering of rocks.
- ______________ can increase the rate of weathering of rock.
- Atmospheric acidity causes the corrosion of some ______________.
- ______________ can increase the rate of corrosion of metals.
- ______________ is found in the stomach.
- ______________ ______________ helps us digest our food.
- Too much stomach acid can cause ______________.
- Some bases are used to relieve ______________ ______________.
- Some ___________ contain too much acid for many plants to grow.
- ______________ is sometimes added to soil to neutralise acidity.
- Acids react with ______________ to give a salt and water.
- Bases react with ______________.
- An ______________ is a base which dissolves in water.
- Metal carbonates are ______________.
- ._____ __________ react with acids to give a salt and carbon dioxide.
- Metal oxides are ______________.
- Metal oxides react with ______________ to give salts and water.
- Some ______________ react with acid to give a salt and hydrogen.
- Acidity is a property of ______________.
- Acids can be identified using ______________.
- Acidity can be measured using the ______________ scale.
- Acidity can be detected using an ______________.
- Alkalinity is a property of ______________.
- Alkalinity can be detected using an ______________.
- Alkalinity can be measured using the ______________ scale.
- Neutral solutions can be identified using ______________.
- Alkalis can be identified using ______________.
- Acids are not ______________ solutions.
- Alkalis are not ______________ solutions.
- pH may be found using universal ______________.
Connecting the up the revision map
You have been given a copy of an outline of a revision map for the topic of acids. This shows some of the things you may have met when you studied acids and bases in your science class. However the map is not complete!
The boxes on the map need to be connected to show how the ideas are linked.
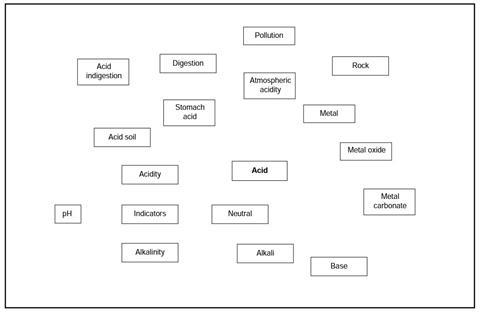
- Look at the outline map. Find two boxes that you think you can connect.
- Draw a clear line between the two boxes.
- Add a label to the line to explain the connection.
- Repeat for as many connections as you can find.
- See if you can think of any other boxes that would fit on this revision map. Draw them in.
- Show the connections for the new boxes in the same ways as above (steps 2 and 3).

Notes
For the full version of this chapter, see downloads below.
Downloads
Revising acids
PDF, Size 0.51 mb
Websites
Additional information
These resources have been taken from the book, Chemical Misconceptions : Prevention, diagnosis and care: Theoretical background, Volume 2, by Keith Taber.

Chemical misconceptions

Discover classroom strategies and activities to tackle common misconceptions among students in chemistry, and explore the theory behind different approaches.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
 Currently
reading
Currently
reading
Revising acids
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36





























































































No comments yet