Support your learners to develop mental models and deepen understanding
This worksheet is part of the Johnstone’s triangle series of resources, designed to help learners to move between different conceptual levels of thinking in key chemistry topics.
Learning objectives
- Describe an ionic compound based on observations.
- Use symbolic models to represent an ionic compound.
- Explain how the bonding in an ionic compound relates to the properties you can observe.
How to use Johnstone’s triangle
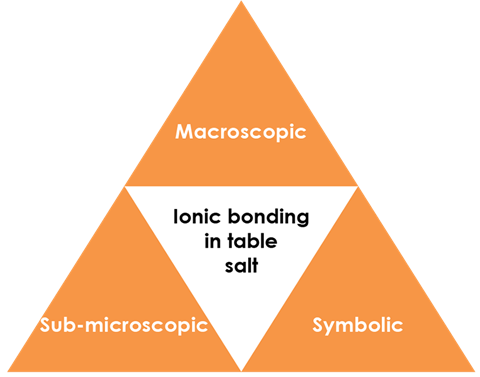
Use Johnstone’s triangle to develop learners thinking about scientific concepts at three different conceptual levels:
- Macroscopic: what we can see. Think about the properties that we can observe, measure and record.
- Sub-microscopic: smaller than we can see. Think about the particle or atomic level.
- Symbolic: representations. Think about how we represent chemical ideas including symbols and diagrams.
For learners to gain a deeper awareness of a topic, they need to understand it at all three levels.
When introducing a topic, do not try to introduce all of the levels of thinking at once. This will overload working memory. Instead complete the triangle over a series of lessons, beginning with the macroscopic level and introducing other levels, in turn, once secure.
All of the levels are interrelated, for example, learners need visual representation of the sub-microscopic in order to develop mental models of the particle or atomic level.
Further reading
Read more about how to use Johnstone’s triangle in your teaching with these articles:
- Develop deeper understanding with models
- Improve students’ understanding with Johnstone’s triangle
- Practical ideas for using Johnstone’s triangle
Norman Reid’s book The Johnstone Triangle: The Key to Understanding Chemistry provides an more in-depth overview, the first chapter is available to read online.
Scaffolding
It is important to share the structure of the triangle with learners prior to use. Tell them why you want them to use the triangle and how it will help them to develop their understanding. Use an ‘I try, we try, you try’ approach when you are introducing Johnstone’s triangle for the first time.
Next steps
To further develop learner’s thinking in all areas of Johnstone’s triangle, try our Developing understanding of ionic bonding worksheet. These include icons in the margin referring to the conceptual level of thinking needed to answer the question.
More resources for teaching ionic bonding
- Use this scaffolded writing activity, Ionic structure and bonding structure strip, to support learners to retrieve and organise their knowledge.
- Steer students away from ionic bonding misconceptions with these ideas for your classroom.
- Get 11–14 students modelling ionic lattices with plasticine.
- Find a set of differentiated Review my learning worksheets with answers, to identify learning gaps and misconceptions on the topic of bonding.
Downloads
Ionic bonding Johnstone's triangle student worksheet
Handout | PDF, Size 0.23 mbIonic bonding Johnstone's triangle teacher notes and answers
Handout | PDF, Size 0.32 mbIonic bonding Johnstone's triangle student worksheet
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.69 mbIonic bonding Johnstone's triangle teacher notes and answers
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.59 mb
























No comments yet