Use this poster and classroom activity to ensure your 14–16 students understand this important industrial application of separation
Crude oil is a mixture of many different compounds. It mainly consists of hydrocarbons – molecules made only of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Hydrocarbons have different uses depending on their properties. Some are useful as fuels and others are used as feedstock – raw materials – for the petrochemical industry where they are used to make products such as polymers, solvents and detergents.
Download this
Infographic poster, fact sheet and differentiated synoptic question worksheets. Put the poster up in your classroom or display it on a projector. Alternatively, print and hand it out.
Use the differentiated synoptic questions to consolidate prior learning on the topics of bonding, structure and the properties of matter and changes of state.
The different hydrocarbons in crude oil must be separated in order to be useful. Fractional distillation separates crude oil into fractions – groups of hydrocarbon molecules with similar carbon chain lengths, properties and boiling points. Each fraction has a different use.
Did you know …?
The oil tankers that carry crude oil to refineries are some of the largest ships and can be over 350 metres long. That’s approximately four football pitches!
The process of fractional distillation
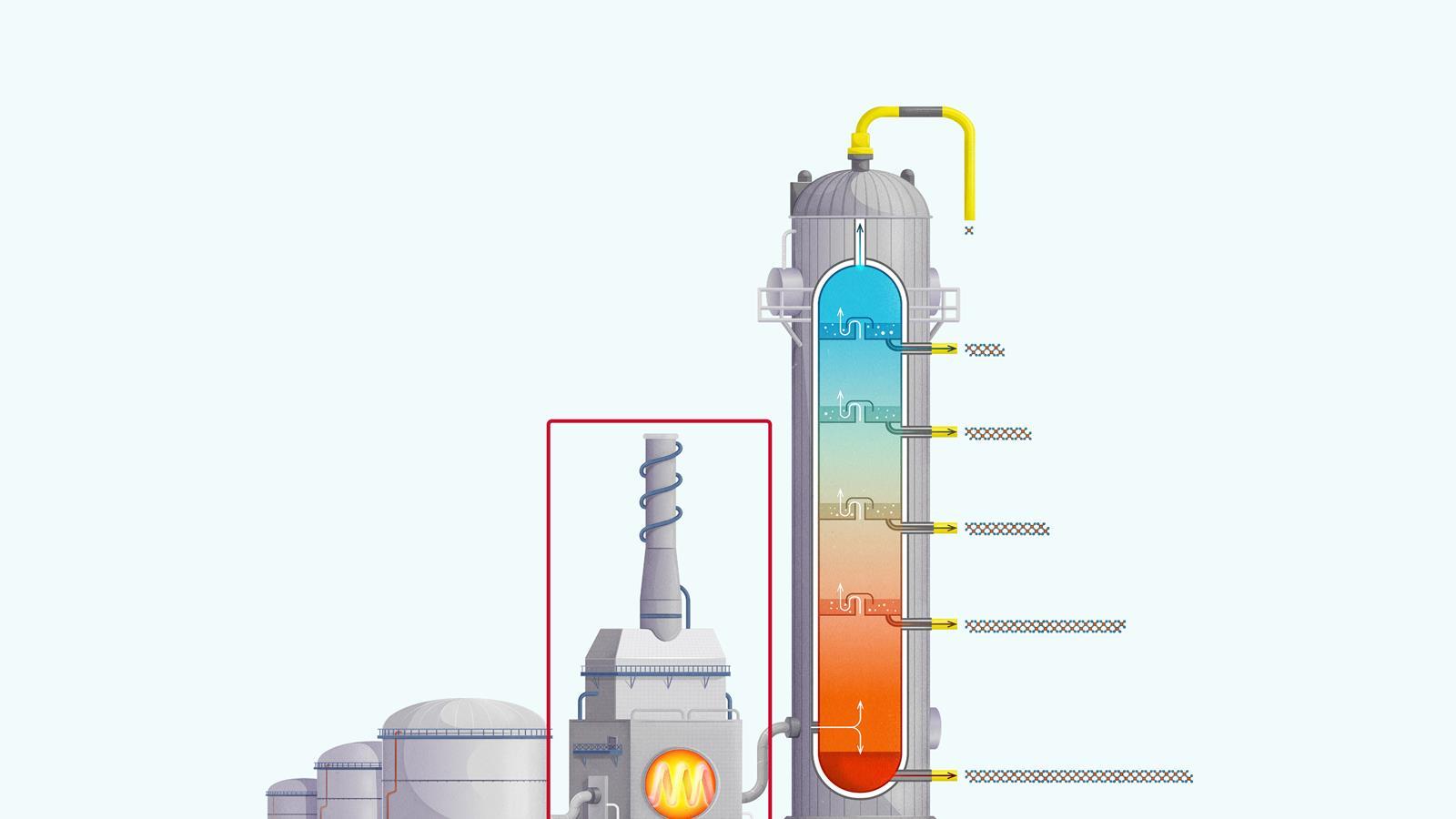
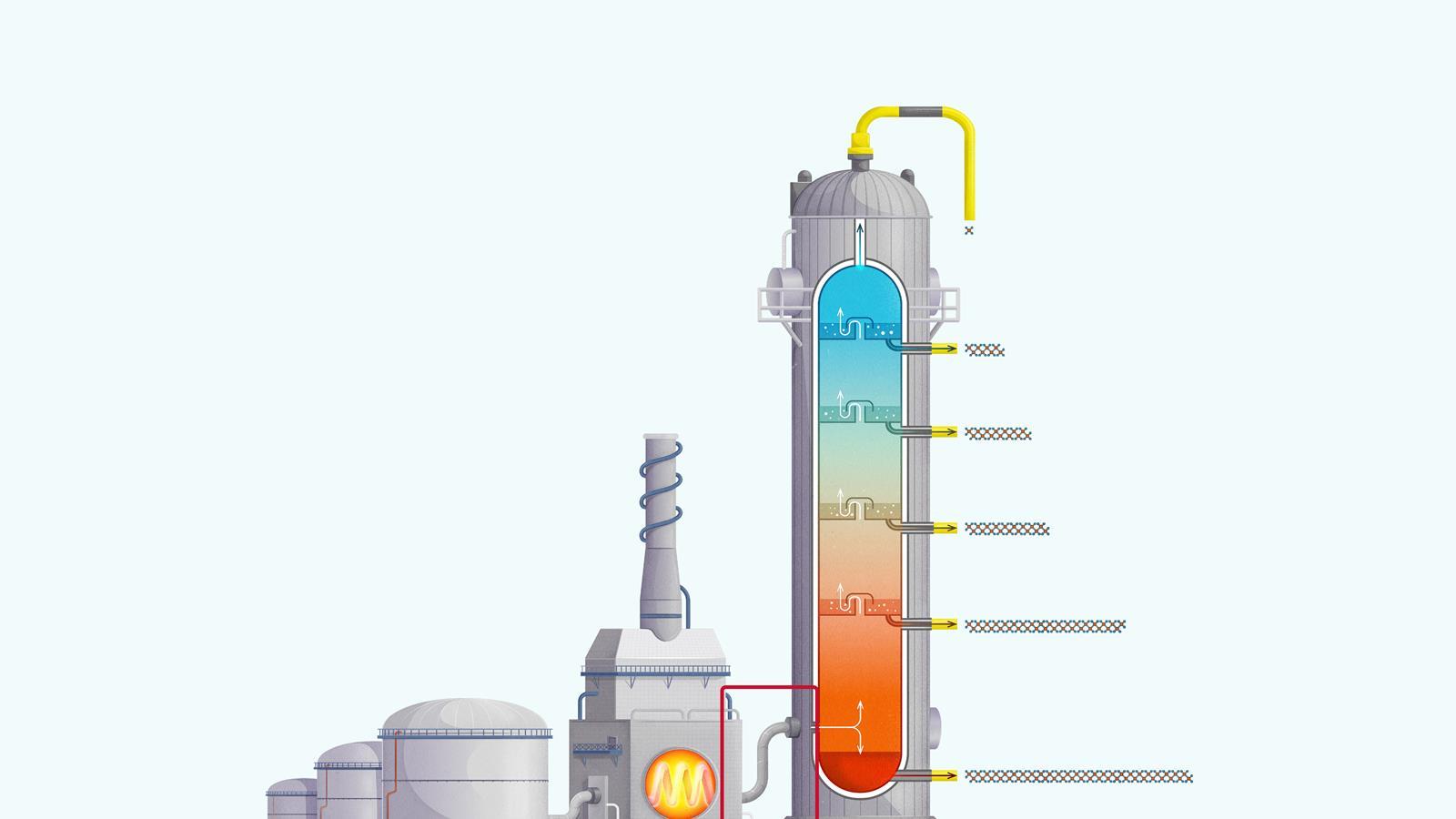
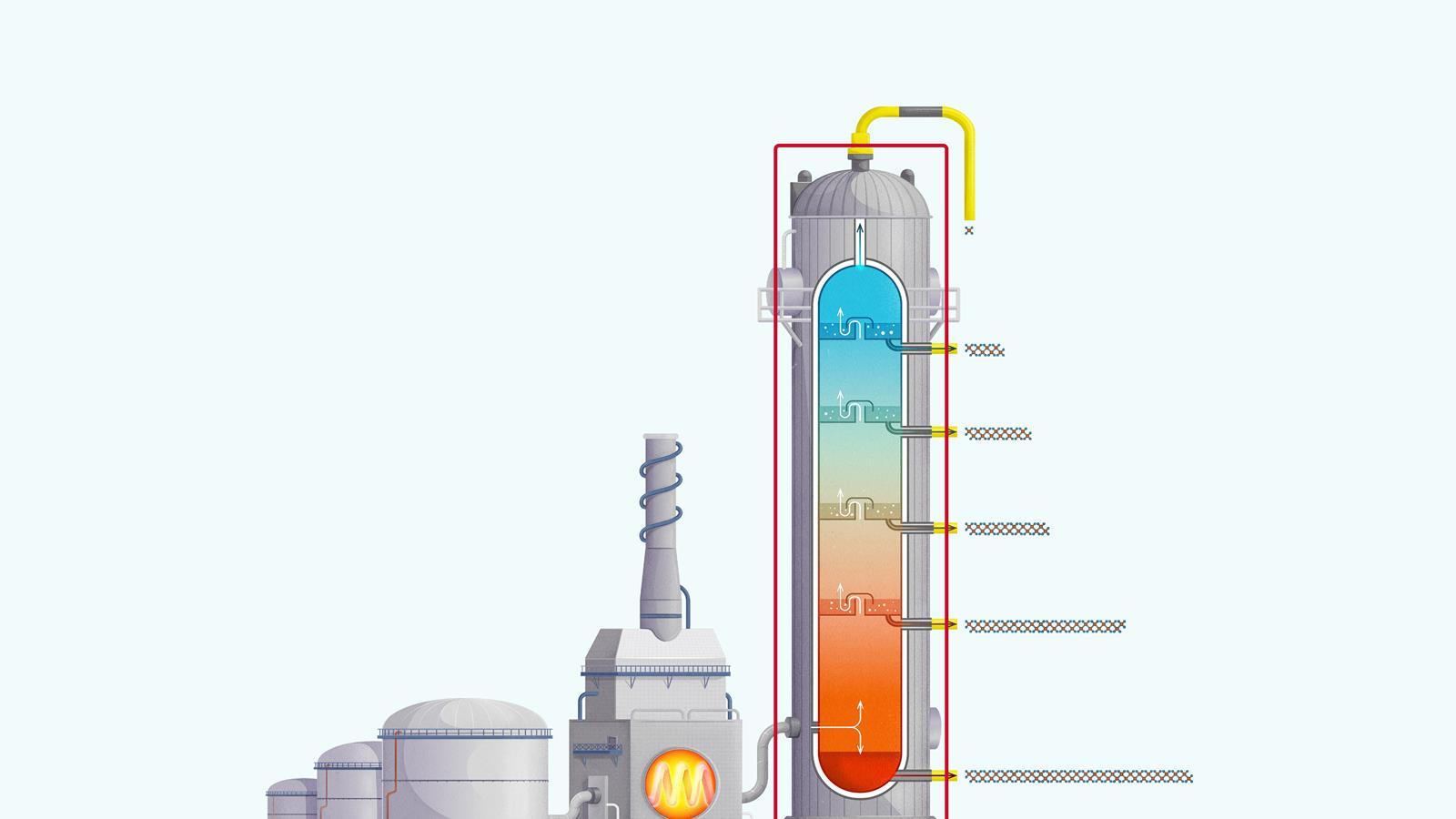
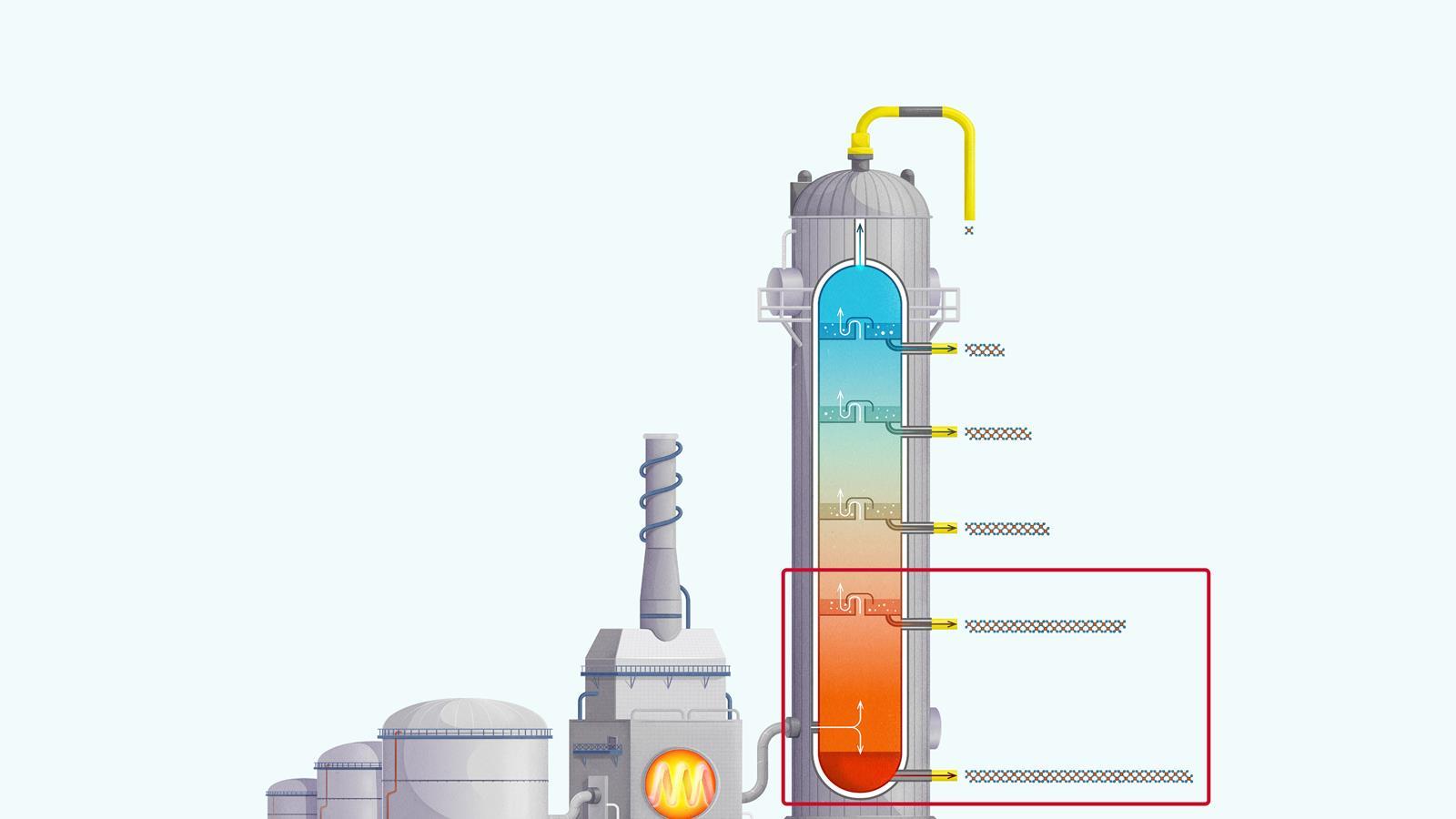
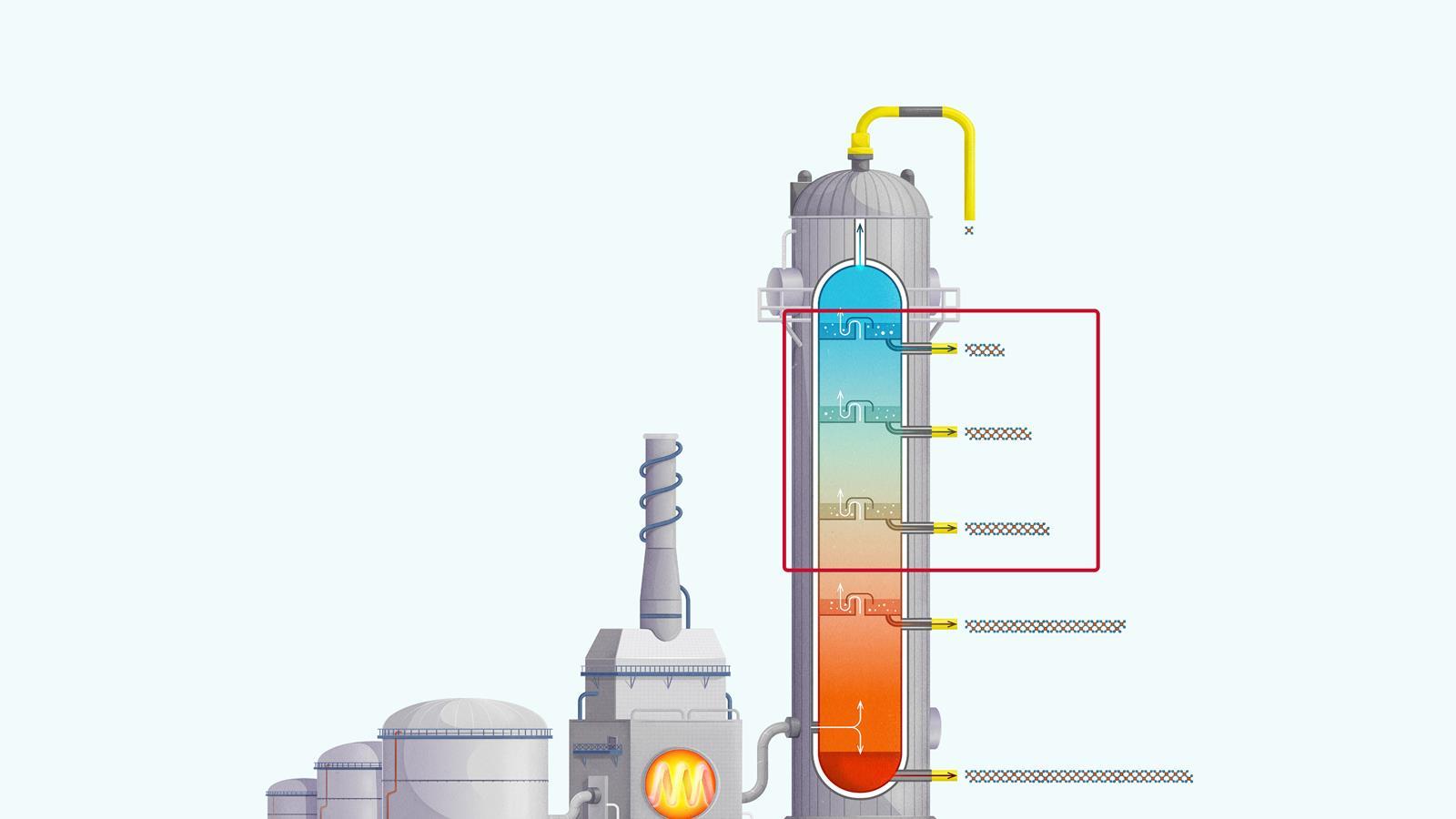
The crude oil is heated in a furnace to over 400ºC. At this temperature, most of the hydrocarbons in the crude oil mixture boil and turn into gas.
The mixture of hot hydrocarbon gases passes into a fractionating column which is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top.
The hot gases rise up the column. Once the temperature of the column falls below the boiling point of a hydrocarbon in the mixture, it is no longer hot enough for the hydrocarbon to stay in gaseous form. The gas therefore condenses and is separated off.
The longer chain hydrocarbons have a higher boiling point and condense towards the bottom of the column where it is hotter.
The shorter chain hydrocarbons have a lower boiling point and remain as gases higher up, only condensing once a lower temperature is reached near the top of the column.
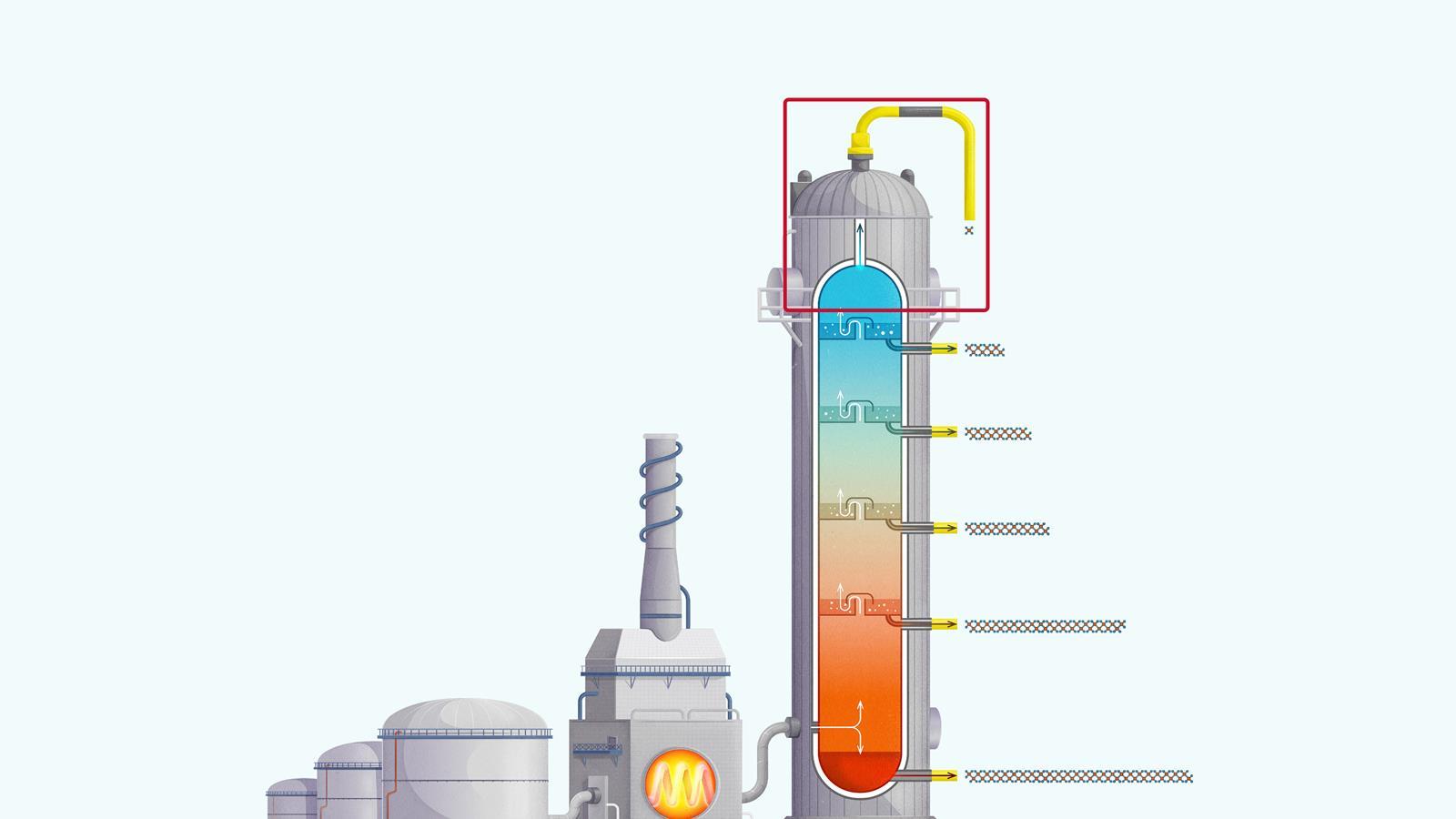
Very short chain hydrocarbons have a boiling point so low they do not condense within the fractionating column and are separated from the top of the column as gases.
Did you know …?
New cars and vans powered wholly by petrol and diesel will not be sold in the UK from 2030.
More resources
- Find out how different lengths of string can be used to model fractional distillation alongside other models to boost understanding.
- Use these differentiated worksheets to assess learners’ knowledge and explore the topic of crude oil, including fractional distillation, fuels and other products from oil.
- Try this class practical or demonstration to simulate the industrial fractional distillation of crude oil.
- Show your students how research and development can happen quickly in the oil and gas industry, when project leaders, like Stuart, get involved.
Fractions
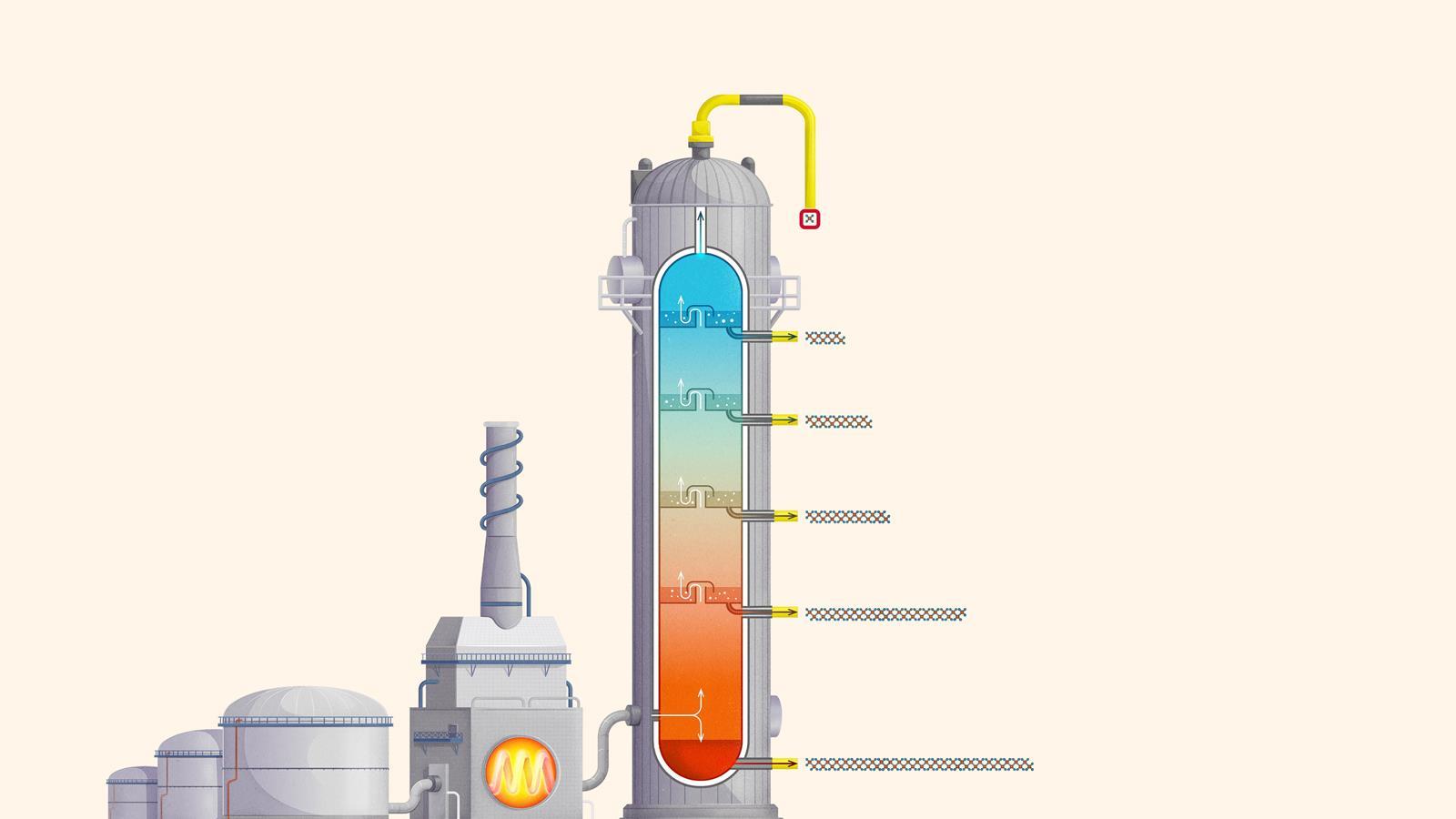
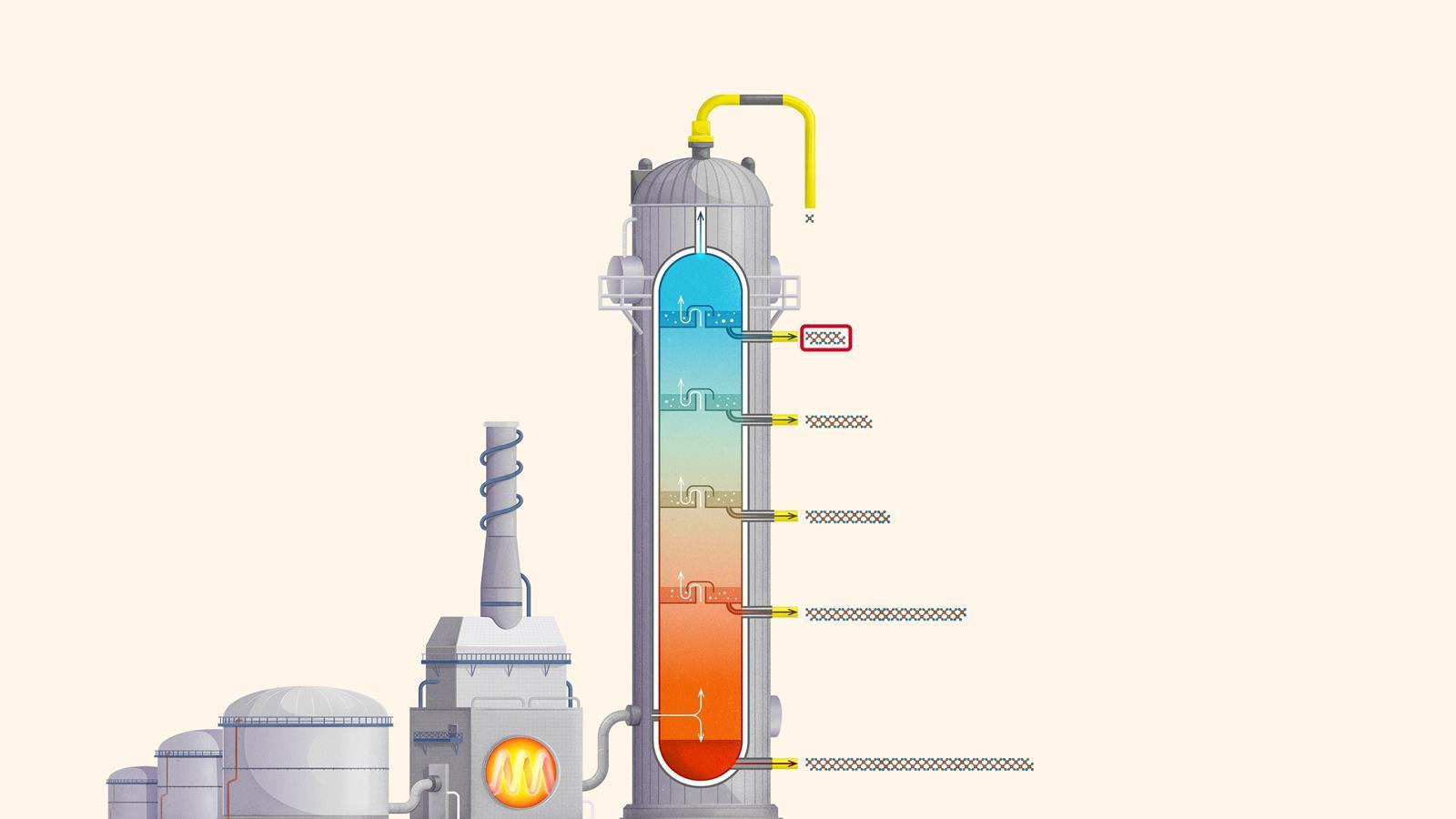
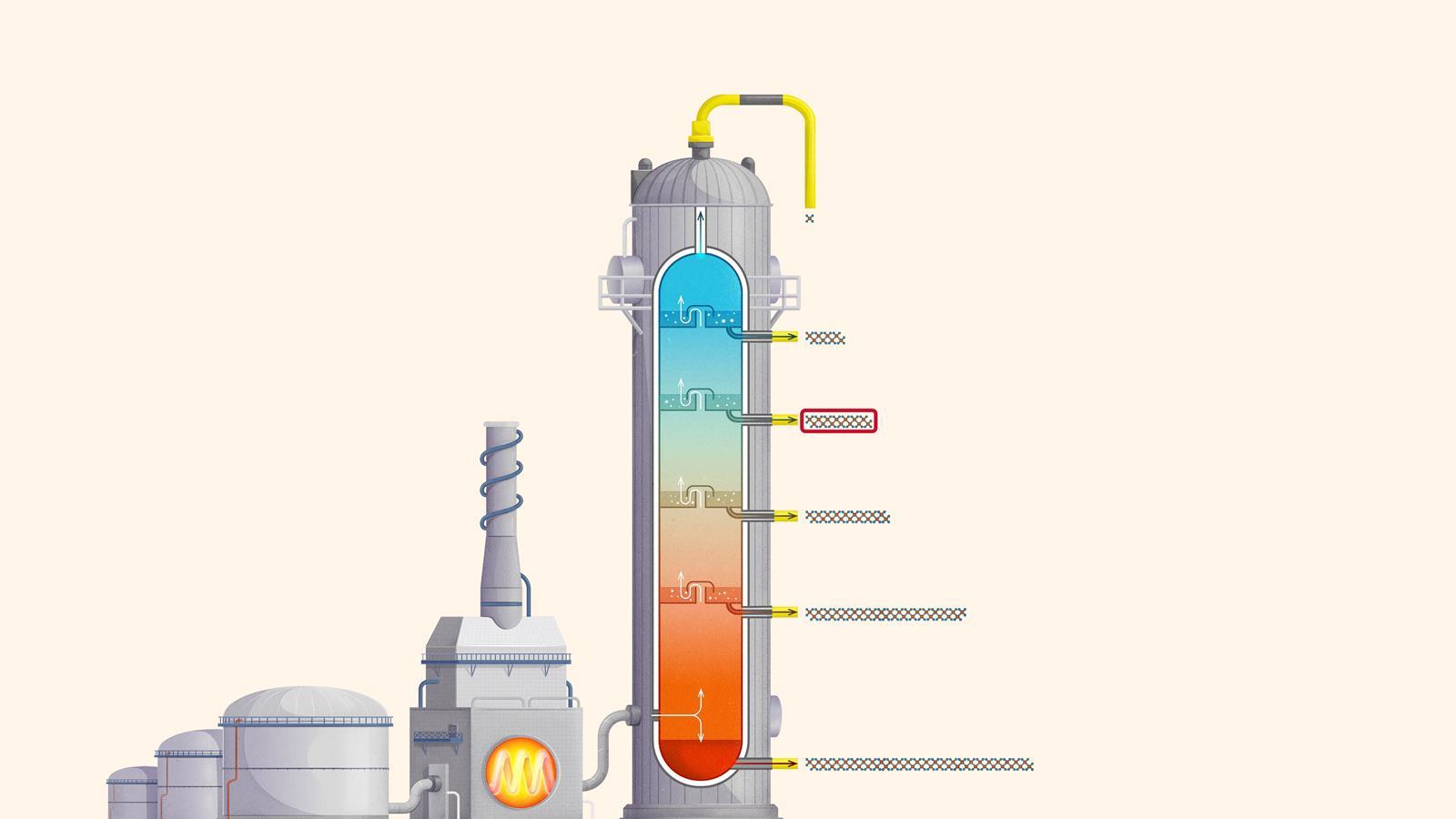
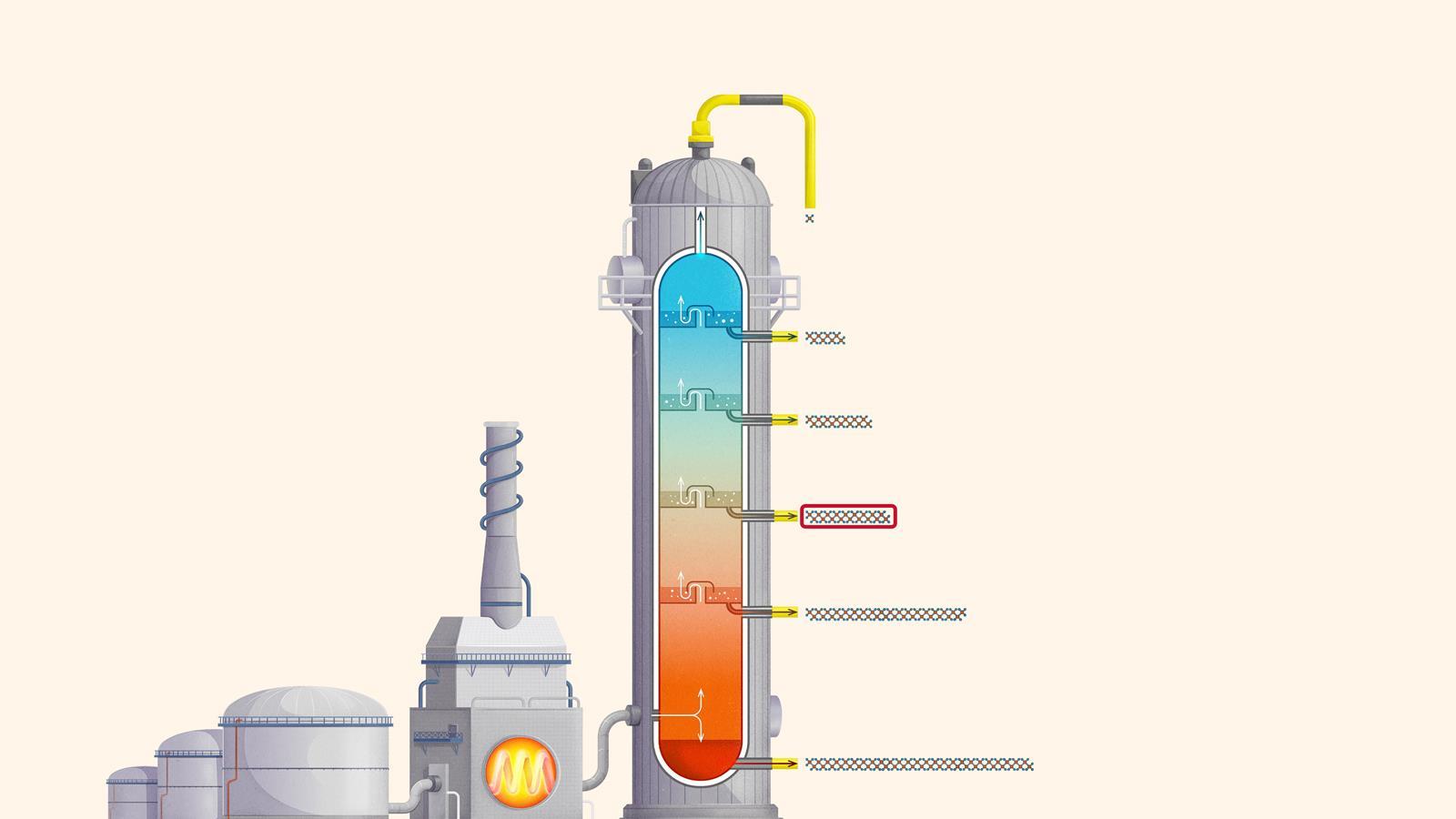
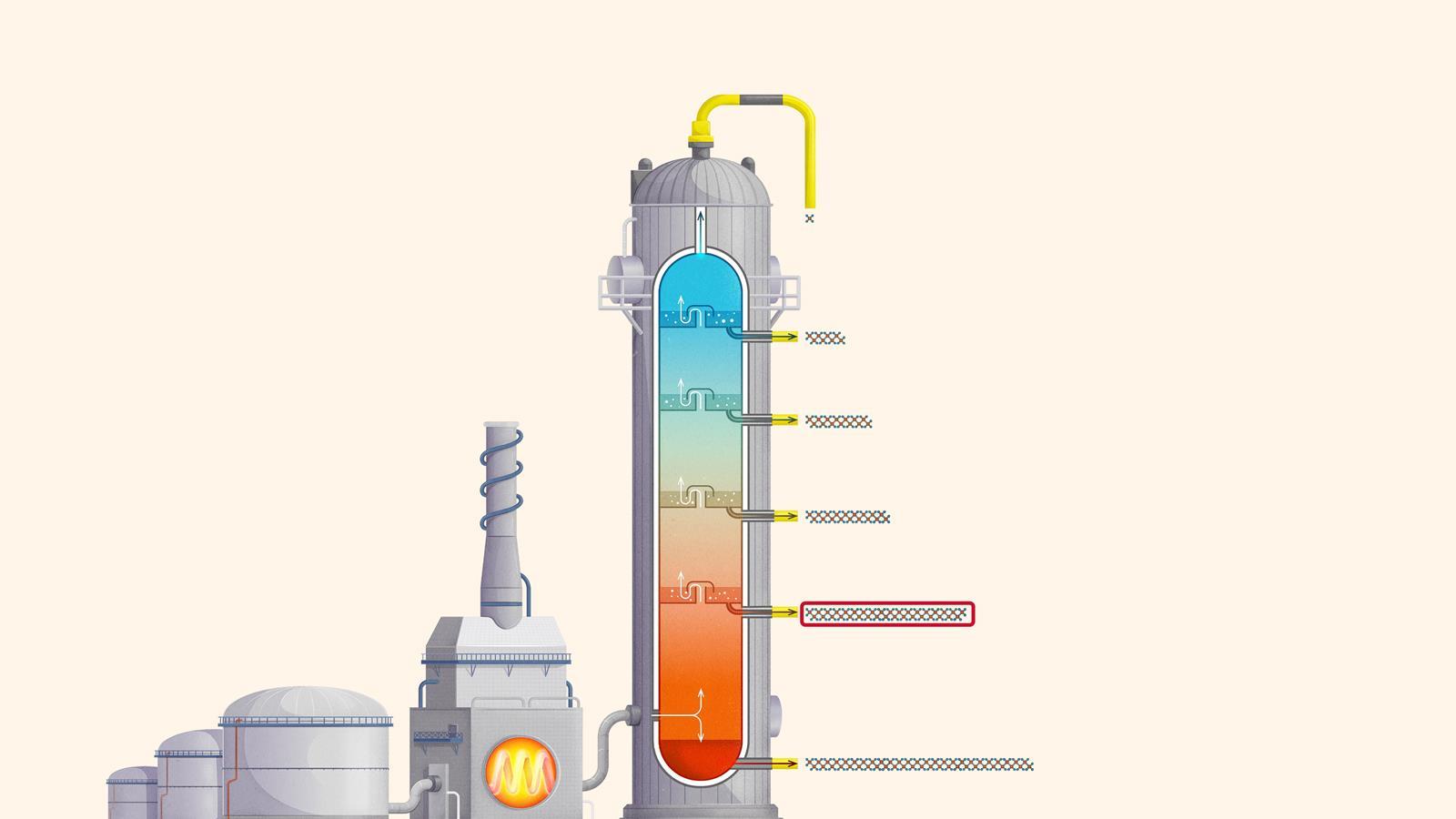
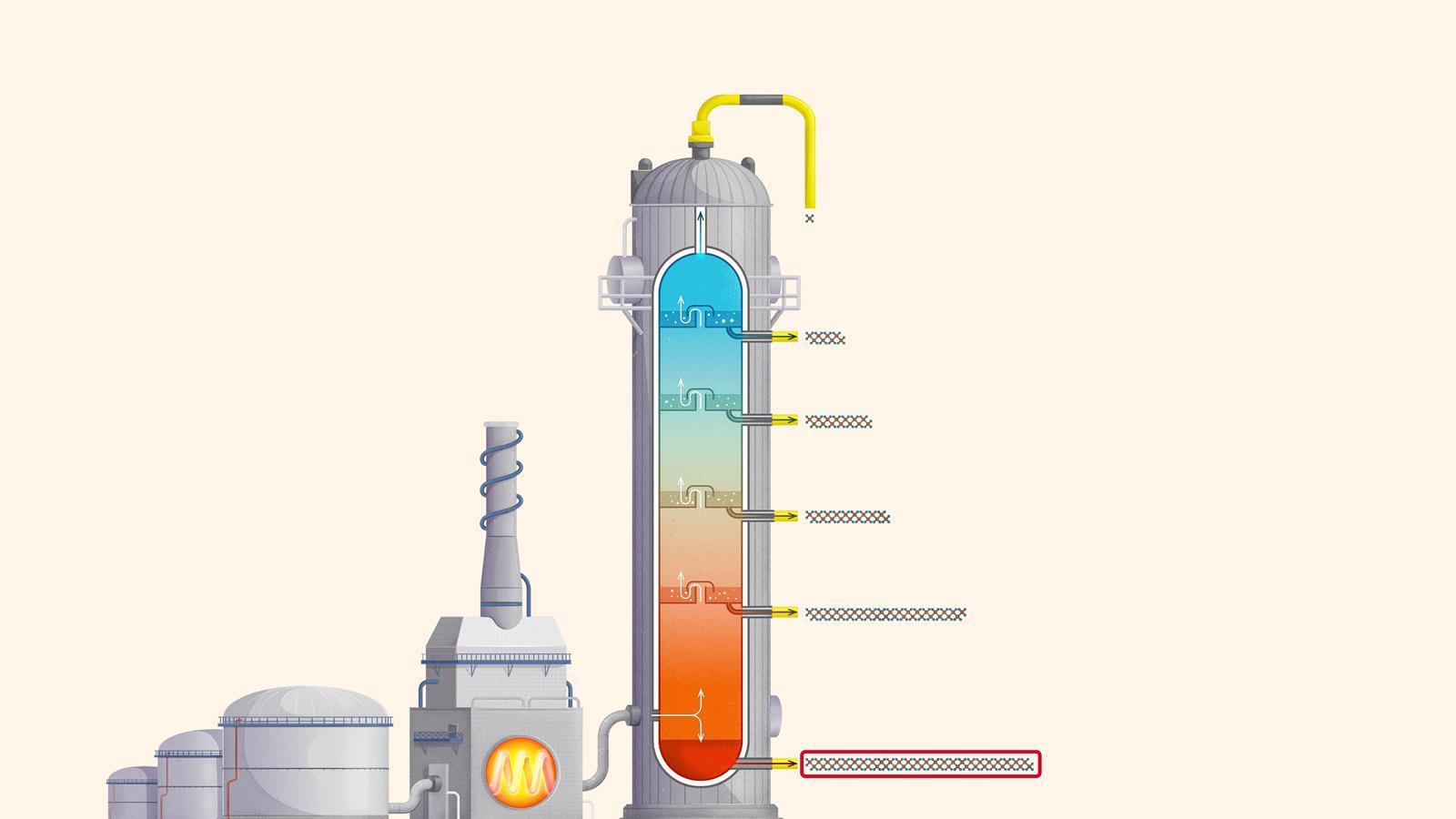
Liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) or refinery gas: mainly consists of propane and butane and is used as bottled gas for cooking and heating
Petrol (gasoline): used as a fuel for car engines
Kerosene: used as a fuel for jet engines in aircraft. Kerosene is also called paraffin in some areas of the world and is used in lamps
Diesel: used as a fuel for cars, vans, lorries and trains
Fuel oil: used as a fuel for ships, for heating and in power stations
Residue (bitumen): used to surface roads and for sealing roofs
Did you know …?
Fractional distillation is also used to separate nitrogen and oxygen from air. The air is first liquefied by cooling to below -200ºC then the gases are separated based on their boiling points (nitrogen -196ºC and oxygen -183ºC).
All illustrations © Dan Bright
Want more posters with activities for your 14–16 students?
Downloads
EiC fractional distillation poster
PDF, Size 0.81 mbEiC fractional distillation fact sheet
Word, Size 0.43 mbEiC fractional distillation fact sheet
PDF, Size 0.16 mbFractional distillation synoptic worksheet (Foundation)
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.47 mbFractional distillation synoptic worksheet (Higher)
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.53 mbFractional distillation teacher guidance (inlcuding answers)
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.43 mbFractional distillation synoptic worksheet (Foundation)
Handout | PDF, Size 0.27 mbFractional distillation synoptic worksheet (Higher)
Handout | PDF, Size 0.3 mbFractional distillation teacher guidance (including answers)
Handout | PDF, Size 0.22 mb











No comments yet