Your 14–16 learners will soon be confidently representing this electrostatic force
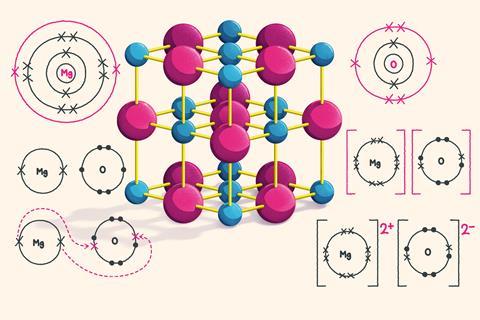
When a metal and a non-metal react, the metal atom loses electrons to become a positively charged ion and the non-metal atom gains electrons to become a negatively charged ion. An ionic bond is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between a metal ion and a non-metal ion due to their opposite charges.
A dot and cross diagram is one way to model the transfer of electrons that occurs during this process.
View and download more infographics
How to draw a dot and cross diagram for magnesium oxide
Magnesium is a metal in group two of the periodic table, so will form a 2+ ion. Oxygen is a non-metal in group six of the periodic table, so will form a 2- ion.
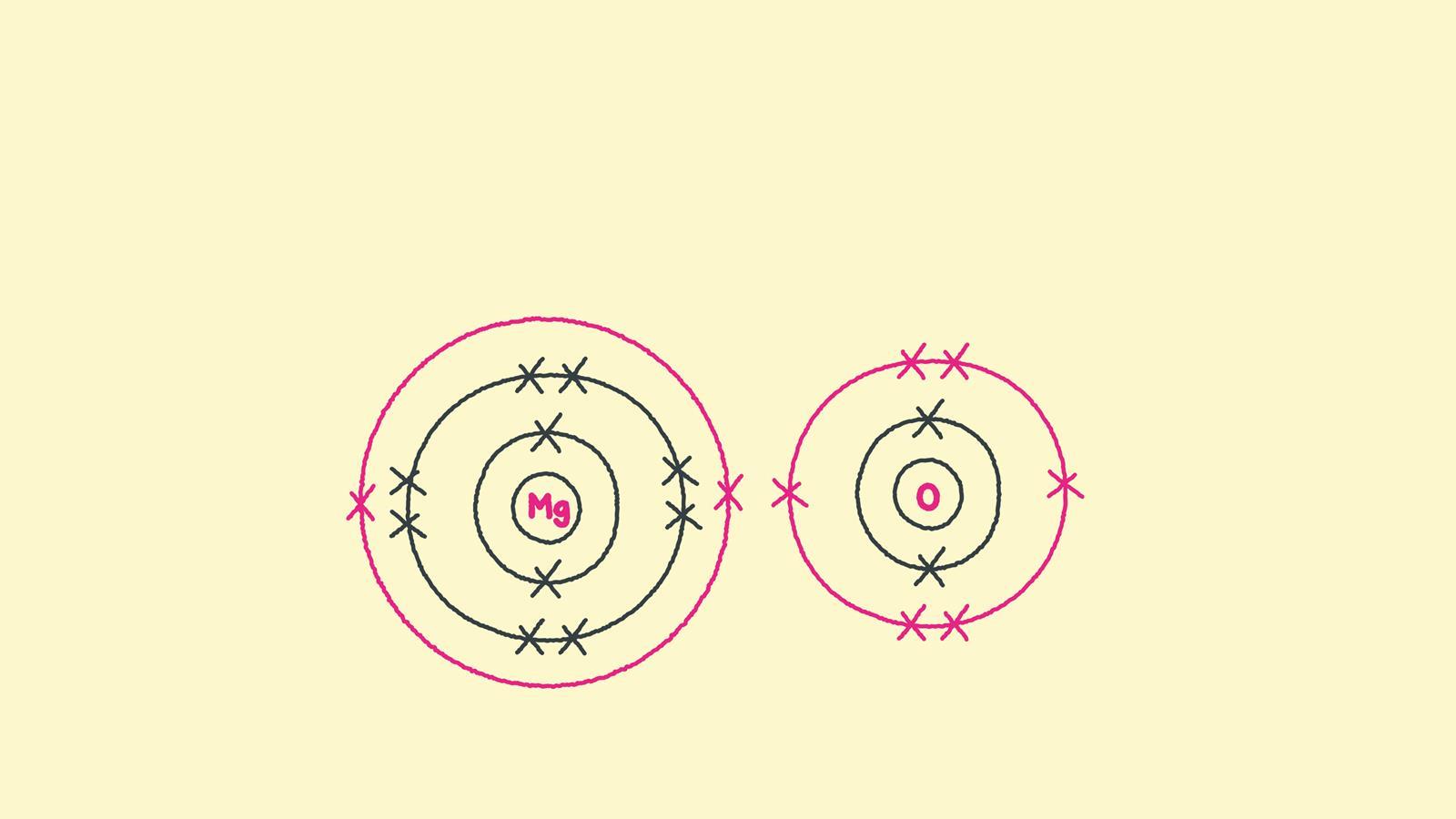
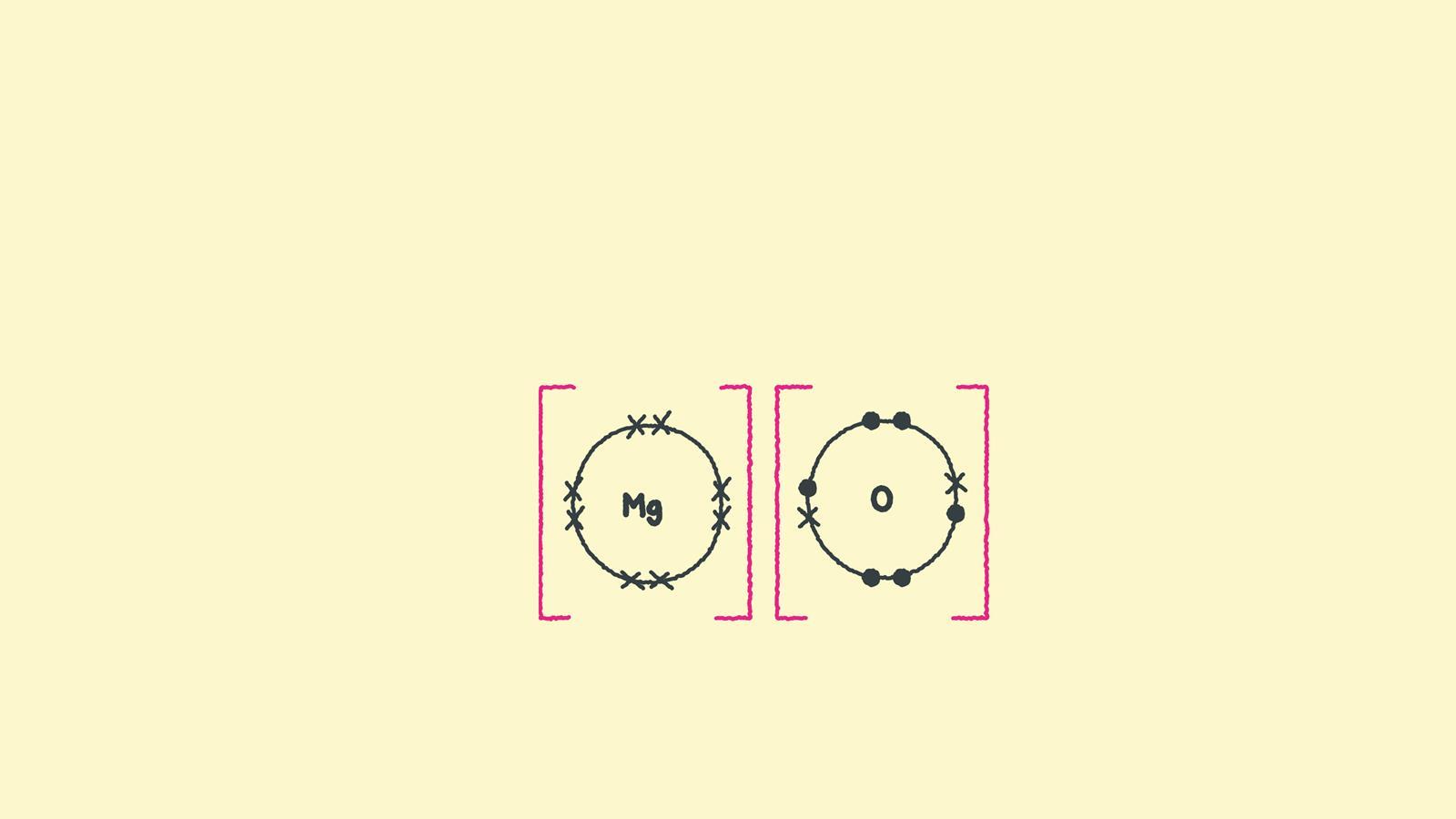
Draw the electron configuration diagram for each atom.
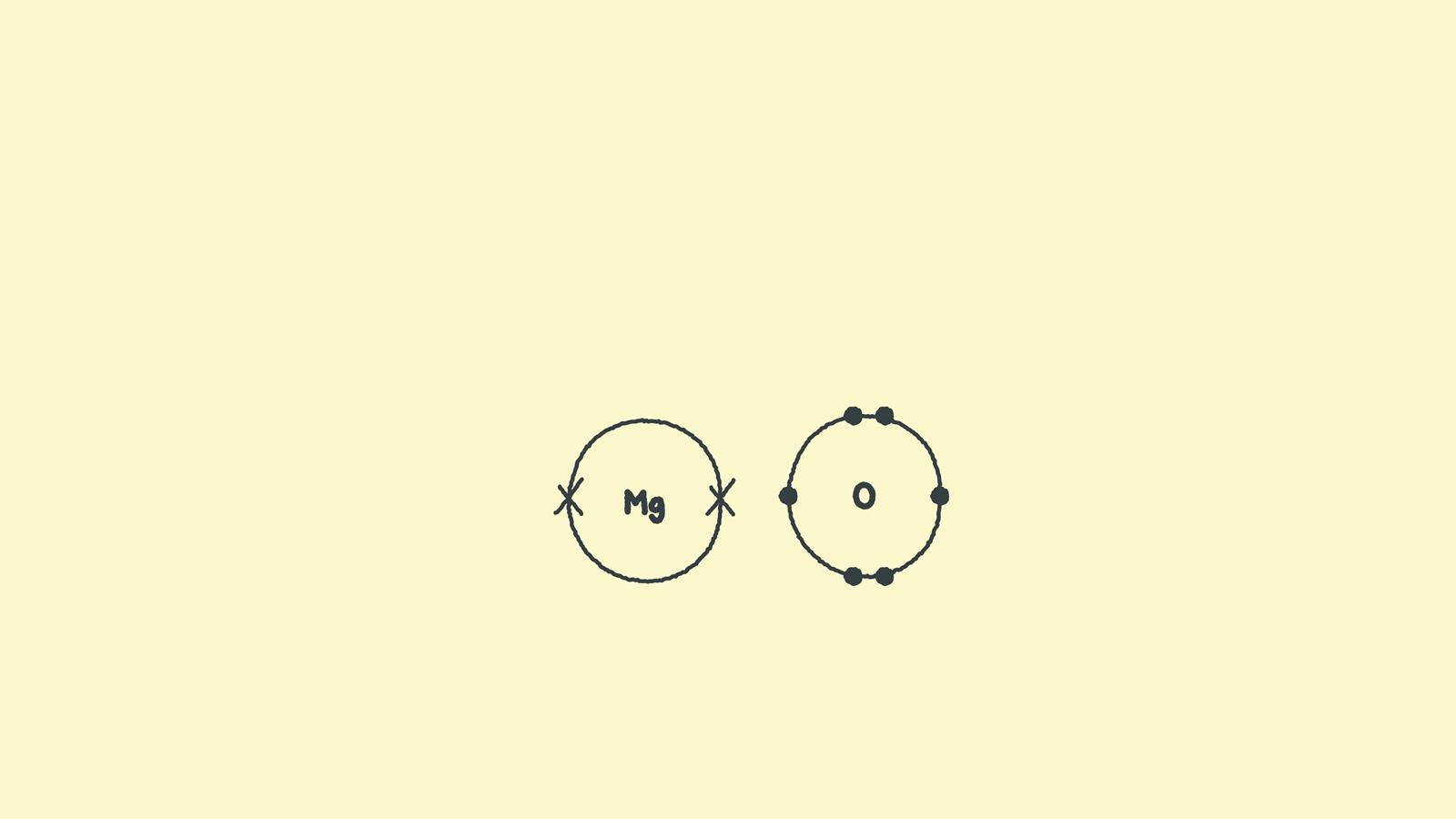
Draw the outer shell of each atom. Magnesium has two electrons in its outer shell, oxygen has six. Swap the crosses for dots in one of your diagrams.
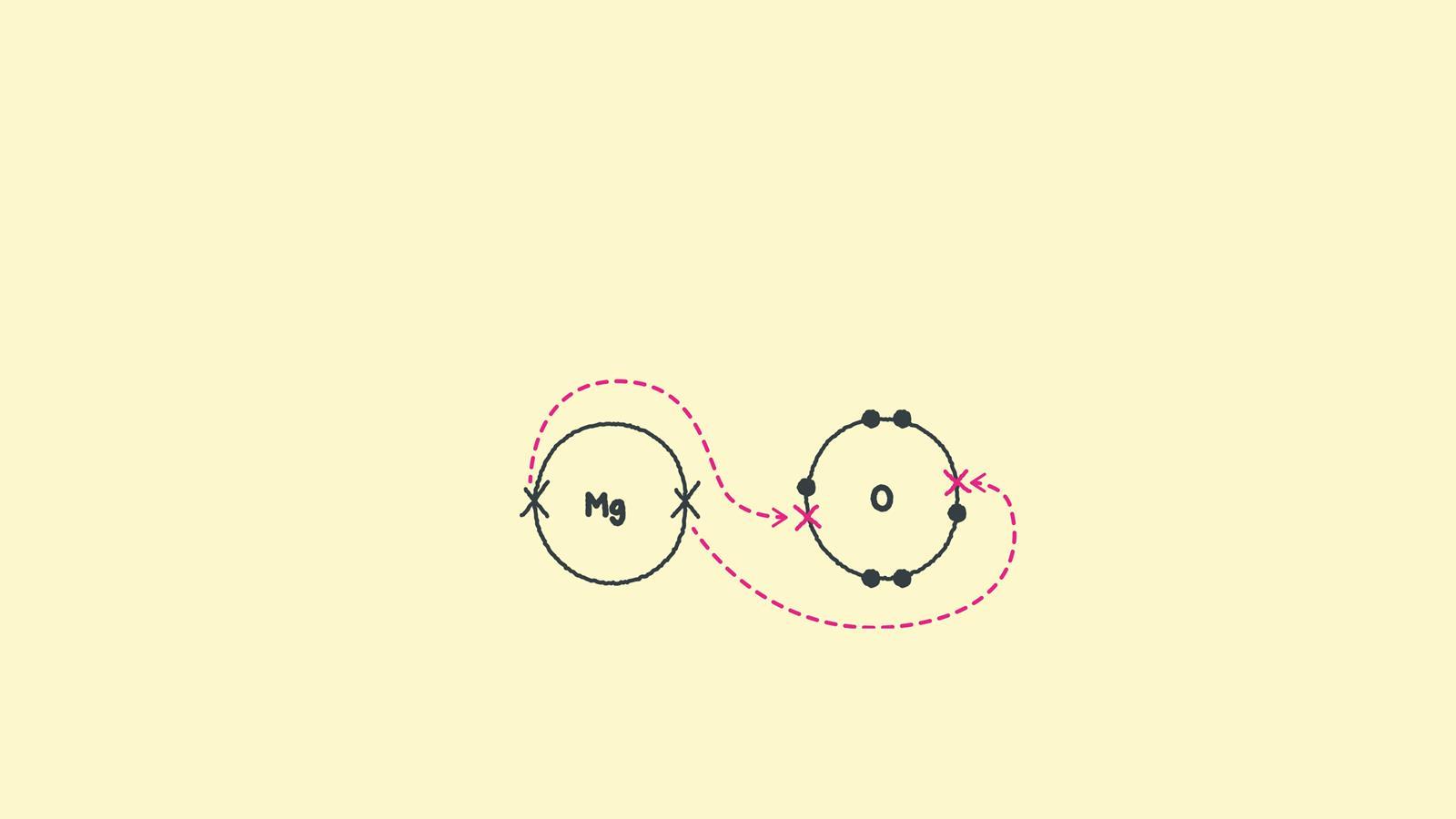
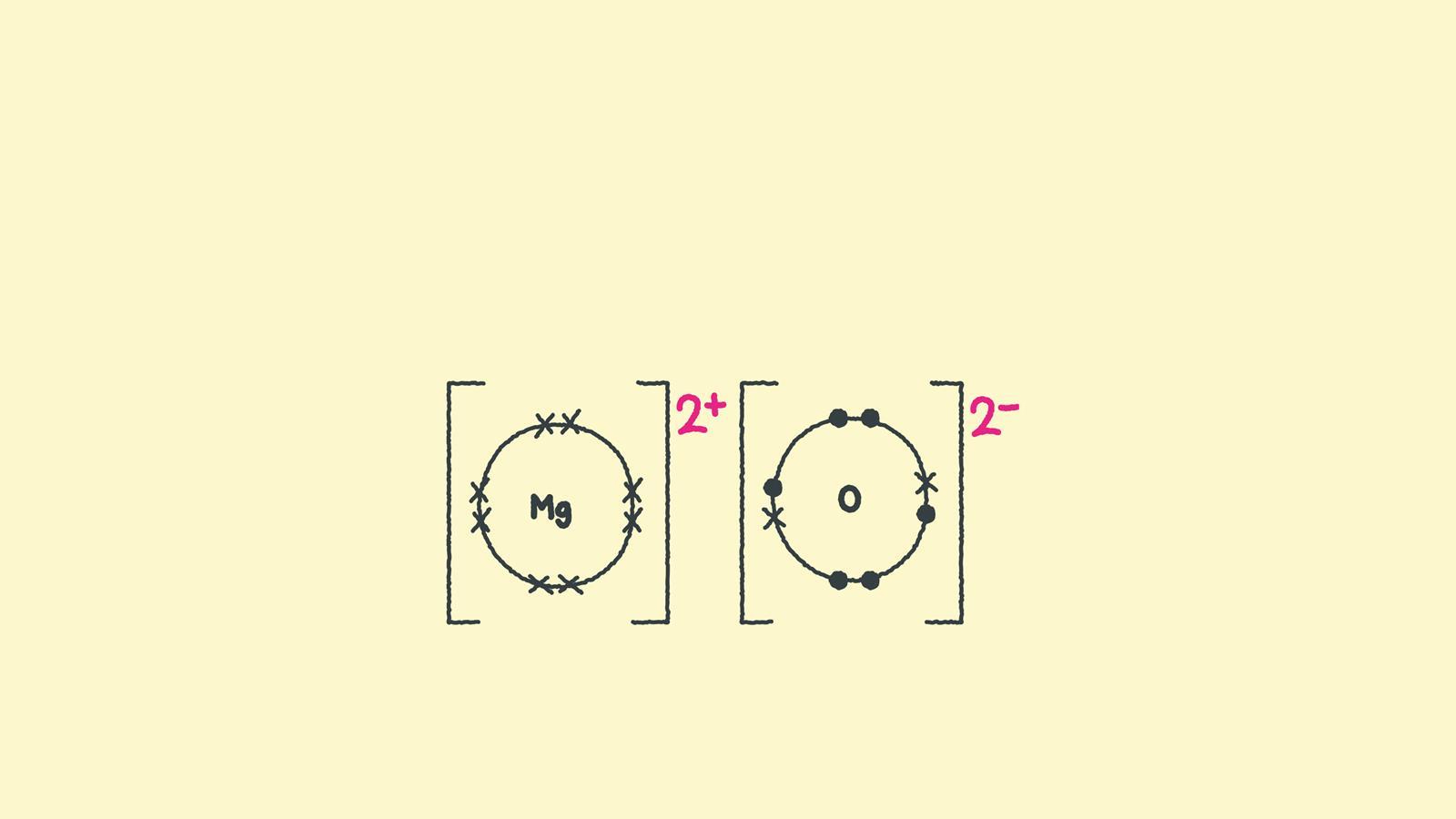
During ionic bonding the atoms form ions by gaining or losing electrons to obtain a full outer shell. Magnesium loses two electrons and oxygen gains two electrons, leaving Mg2+ and O2-.
Draw a square bracket around each ion. Magnesium now has an empty third shell so draw the second shell instead.
Add the charge outside the brackets at the top right corner. Write the size of the charge first, followed by the plus or minus.
Did you know …?
- The group number on the periodic table tells you how many electrons there are in the outer shell of the atom. You can use this to work out the charge of the ion.
- The charge is distributed throughout the ion, the square brackets denote this.
- In an ionic compound the metal ion doesn’t just form a bond with the ion it donated electrons to. It forms strong ionic bonds with any ions of opposite charge that fit close enough to it in the ionic lattice.
- Magnesium oxide is not soluble in water because the attraction between the polar water molecules and the ions is not strong enough to break the ionic bonds between the magnesium and oxygen ions.
Drawing more complex ionic compounds
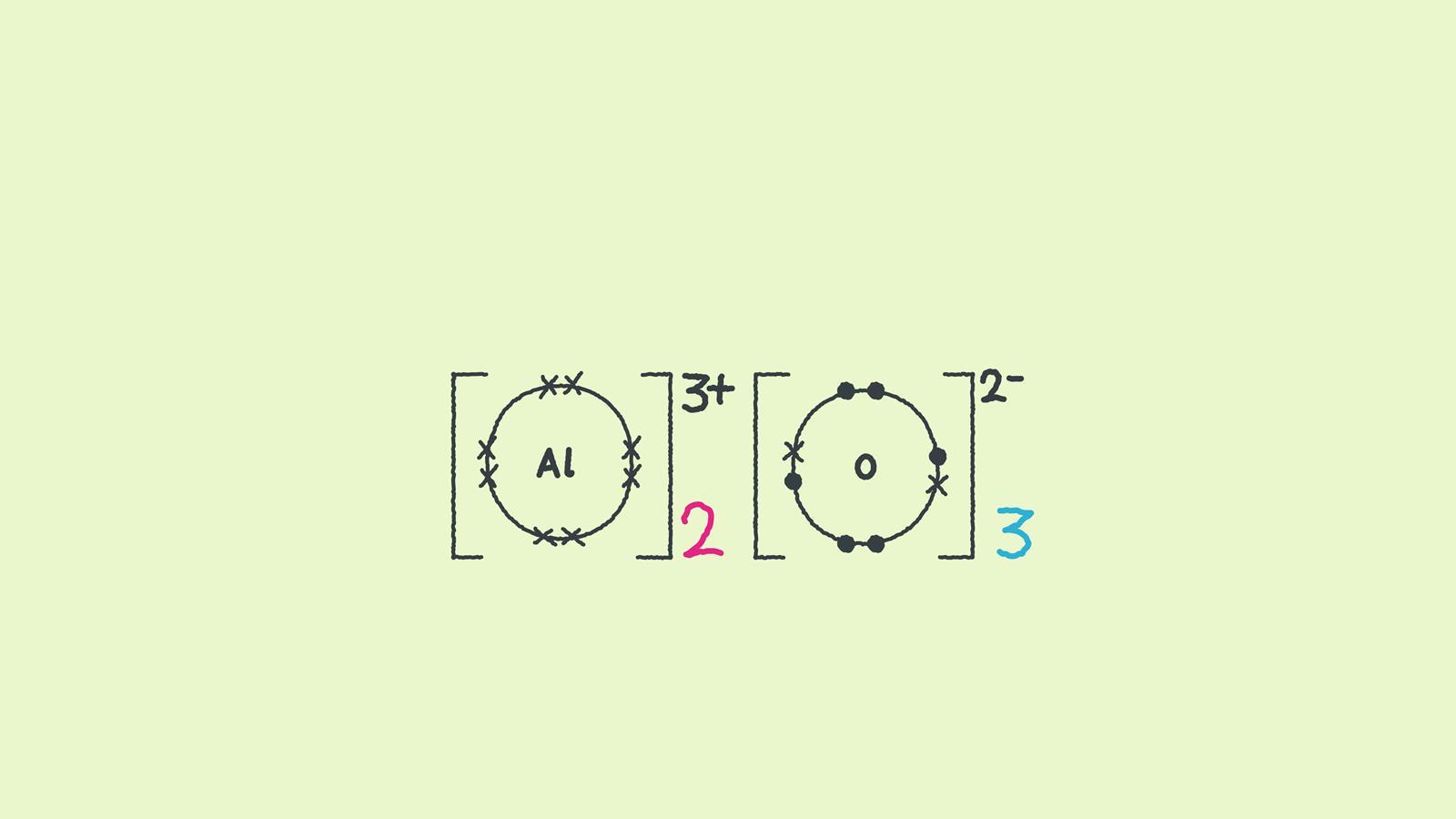
In magnesium oxide, the charges on the metal and non-metal ions are equal and opposite. What happens when the charges on the ions are not equal in magnitude? In aluminium oxide the charge on the positive metal ions is 3+ while the charge on the negative oxide ions is 2-. Here are some different ways to draw aluminium oxide (Al2 O3).
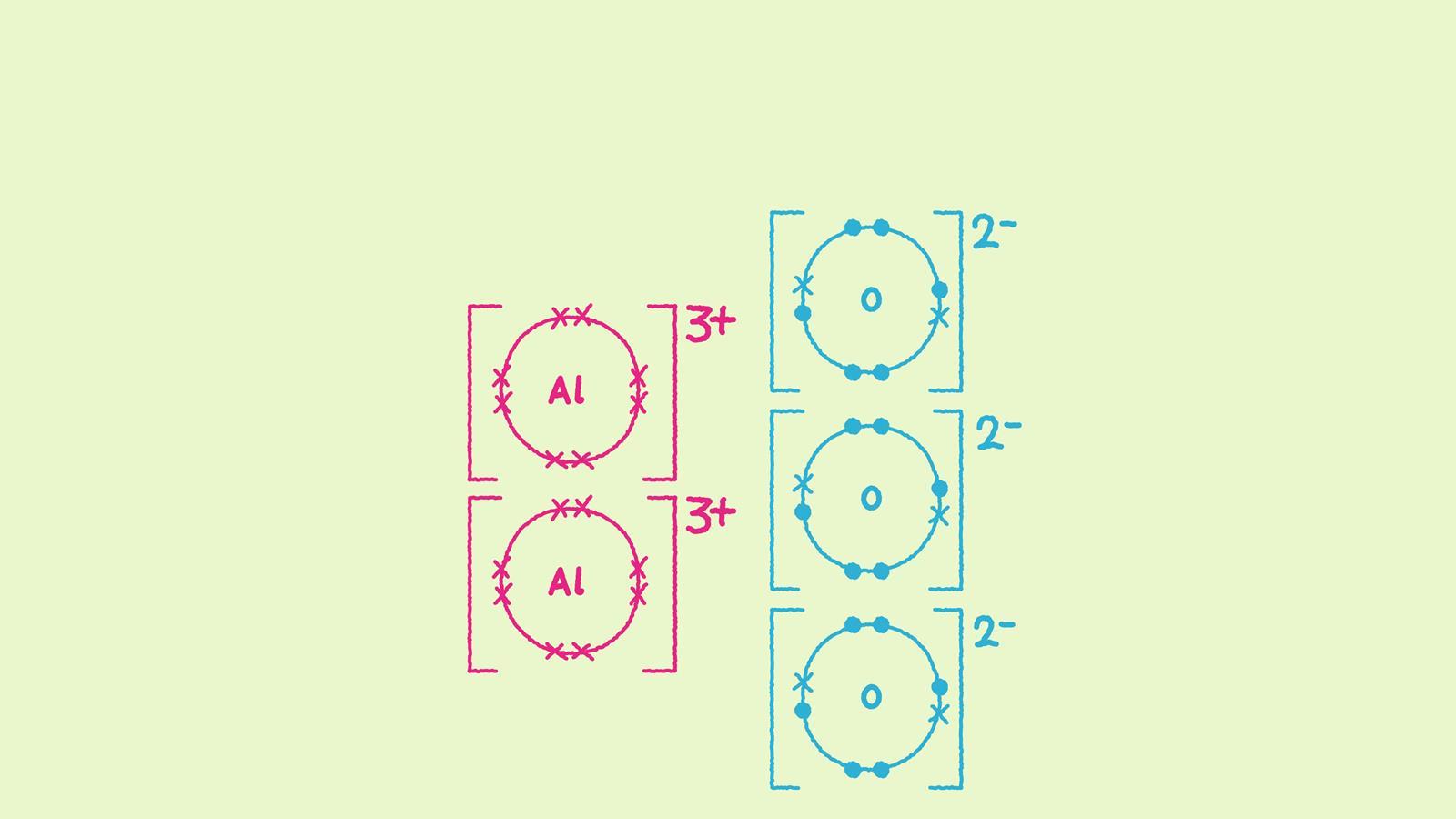
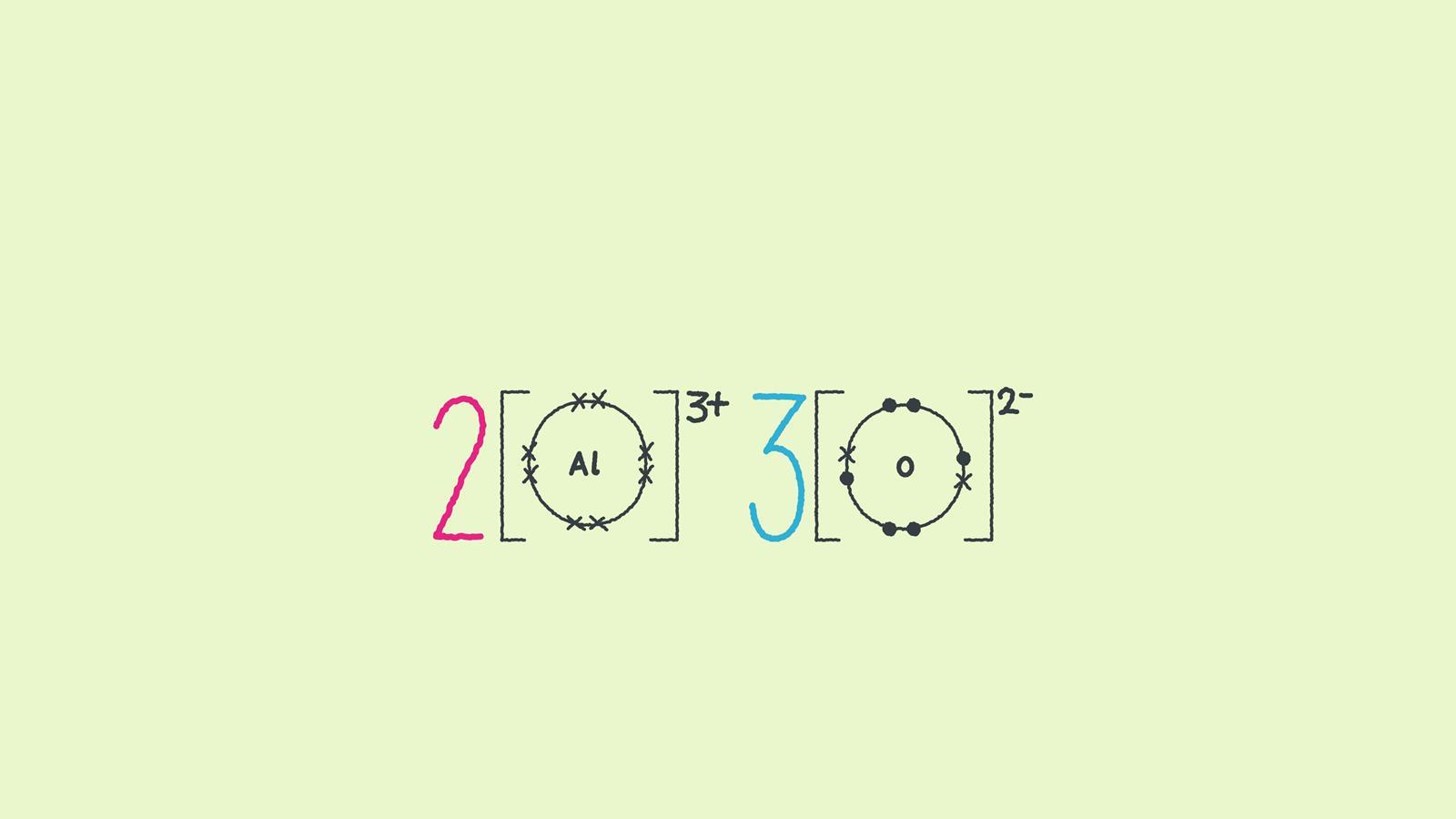
The number of ions indicates the ratio of aluminium to oxygen.
This diagram looks more like the chemical symbol for the compound Al2O3.
The large numbers in this diagram are multipliers. They mean that there are two aluminium ions for every three oxygen ions.
All illustrations © Dan Bright
Want more step-by-step guides? Check out these articles with resources on:
Downloads
Ionic bonding mats student sheet
Handout | PDF, Size 0.53 mbIonic bonding mats student sheet
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.87 mbIonic bonding mats teacher notes
Handout | PDF, Size 1.01 mbIonic bonding mats teacher notes
Editable handout | Word, Size 1.62 mbIonic bonding dot and cross diagrams poster
Handout | PDF, Size 1.13 mbIonic bonding diagrams fact sheet
Editable handout | Word, Size 0.54 mbIonic bonding diagrams fact sheet
Handout | PDF, Size 0.26 mb



























4 readers' comments