All Feature articles – Page 28
-
 Feature
FeatureFighting skin cancer with prodrugs
Prodrugs - selective chemical agents - are beginning to show potential as a cure for skin cancer
-
 Feature
FeatureWhich chemistry course?
Selecting the right chemistry course and the right institution are paramount in a prospective chemist's life
-
 Feature
FeatureWho really discovered the Haber process?
Although Fritz Haber's name is now attached to the process for the synthesis of ammonia from its constituent elements by using high pressure, who was responsible for this reaction?
-
 Feature
FeatureMaking triazoles, the green way
Triazole synthesis provides an excellent example of a reaction that has the potential to illustrate principles of green chemistry to undergraduates
-
 Feature
FeatureUS chemical education going green
Kathryn Roberts meets Mary Kirchhoff, the new director of education at the American Chemical Society (ACS) in Washington DC
-
 Feature
FeatureMicroscale chemistry
The range of school experiments being done on the microscale is growing. Here are examples from Key Stage 3, through Key Stage 4, to A-level
-
 Feature
FeatureDealing with nuclear waste
Nuclear power is a low-carbon technology, but it does come with a catch: it produces waste that emits harmful radiation for many thousands, even millions of years. UK chemists, however, are working to produce materials and technology to deal with this problem.
-
 Feature
FeatureFlu drugs - pathway to discovery
If bird flu ever starts to transmit from human to human, with no effective vaccine available our only defence will be the antiviral drugs Relenza and Tamiflu
-
 Feature
FeatureMendeleev - the man and his legacy...
A look at the life and work of Russia's most famous chemist, who died 100 years ago
-
 Feature
FeatureThe periodic tables of Mendeleev
How Mendeleev corrected the atomic weights of In, Ce and U, and thus constructed the remarkable Periodic Table of 1871
-
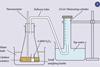 Feature
FeatureInvestigating activation energies
A challenge for post-16 students to investigate the activation energies of the enzyme-catalysed and the inorganic-catalysed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
-
 Feature
FeatureMolecular computers - tomorrow's technology?
As the miniaturisation of silicon chips fast approaches its limit chemists are copying Nature in attempt to build computers atom by atom, molecule by molecule
-
 Feature
FeatureDrugs for dementia
About 10 per cent of men and women over 65, and nearly half of those over 80, have Alzheimer's disease
-
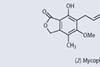 Feature
FeaturePhenols in medicine
Phenol encountered in school or college chemistry laboratories demands special respect on account of its toxic and corrosive nature. But phenol and its derivatives do have a few medicinal surprises
-
 Feature
FeatureAncient coins
Chemistry has played its part in numismatics - in the manufacture, analysis, aesthetics and conservation of coinage
-
 Feature
FeatureApplied science: on course
Applied science has a key role in the 14-16 curriculum, and its popularity is growing
-
 Feature
FeatureNatural products - back in vogue
Chemists are once again turning to Nature to replenish the medicine chest
-
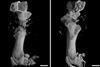 Feature
FeatureGlass bones
'Bioactive' ceramic and glass alternatives could improve the quality of life for millions of people suffering from osteoporosis
-

-
 Feature
FeatureA forgotten anniversary?
Has the significance of William Henry Perkin's synthesis of the purple dye mauveine begun to fade?











